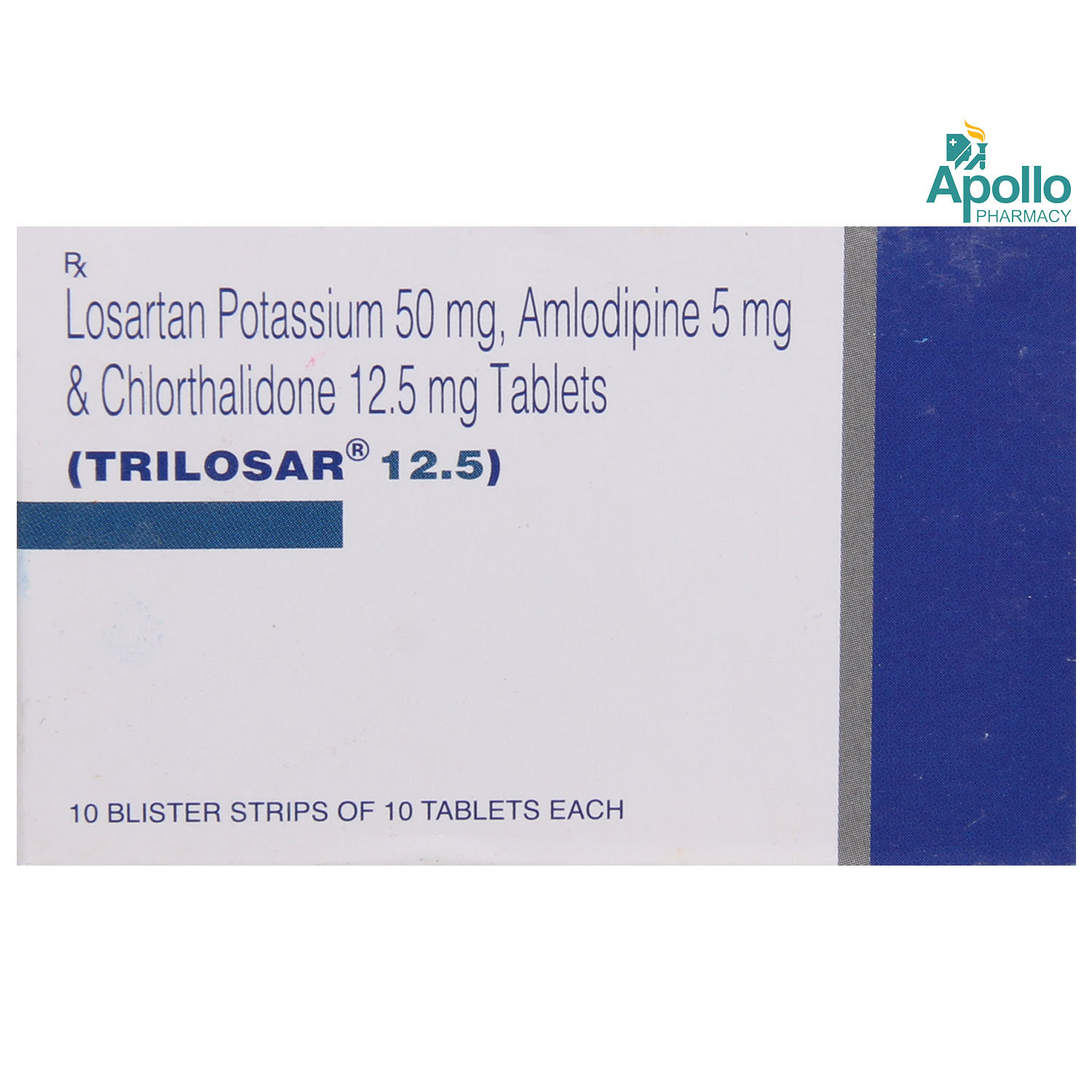
TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET




MRP ₹119
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹17.9 Cashback (15%)
know your delivery time
Provide Delivery Location
Composition :
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :

Secure Payment

Trusted by 8 Crore Indians

Genuine Products
Therapeutic Class
Country of origin
Manufacturer/Marketer address
Disclaimer
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
You are recommended not to consume alcohol along with TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET to avoid unpleasant side-effects.
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET is not recommended during pregnancy unless your doctor considers it essential. Your doctor will weigh the benefits and any potential risks before prescribing it to you.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET should not be used when breastfeeding unless clearly necessary. Your doctor will weigh the benefits and any potential risks before prescribing it to you. Please consult your doctor.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
It is not recommended to drive after taking TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET as it may occasionally cause drowsiness.
Liver
Consult your doctor
TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET to be taken with caution, especially if you have a history of liver diseases/conditions. Your doctor may adjust your dose depending upon your current kidney conditions.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET to be taken with caution, especially if you have a history of kidney diseases/conditions. Your doctor may adjust your dose depending upon your current kidney conditions.
Children
Safe if prescribed
TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET to be taken with caution, especially if you are children below the age of 12. Your doctor may adjust your dose depending upon your age.
Product Substitutes
About TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET
TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET belongs to a group of medicines known as anti-hypertensives, primarily used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and oedema (a buildup of fluid in the body). Hypertension or high blood pressure is a lifelong or chronic condition in which the force exerted by the blood against the blood vessel (arteries wall) increases. The higher this blood pressure, the harder the heart has to pump. Oedema may occur in high blood pressure where fluids of the body get trapped in the tissues of the hands, arms, feet, ankles and legs, leading to swelling.
TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET contains Chlorothiazide, Losartan and Amlodipine. Chlorothiazide is a diuretic that works by increasing the amount of urine passed out from the kidneys. It effectively reduces excess fluid levels in the body and treats Edema (swelling) associated with heart, liver, kidney or lung disease. Amlodipine is a calcium channel blocker, and Losartan is an angiotensin receptor antagonist. Both work by relaxing and widening the blood vessels. This, in turn, reduces the heart's workload and makes the heart more efficient at pumping blood throughout the body. So, it helps to lower high blood pressure, reducing the chances of heart attack or stroke.
Take TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET as prescribed by your doctor. Depending on your medical conditions, you are advised to take TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET for as long as your doctor has prescribed it for you. You may experience glucose intolerance (low or high level of glucose), ankle swelling, sleepiness, headache (sense of heat in the face, ears, neck, and trunk), flushing, tiredness, nausea, decreased potassium level in the blood, Increased blood uric acid and altered blood lipid level. Most of these side effects of TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET do not require medical attention and gradually resolve over time. However, if the side effects are persistent, reach out to your doctor.
Try not to stop taking this medicine of your own. Tell your doctor about this, as it may cause a rise in blood pressure and increase the risk of heart complications like stroke and heart disease. Inform your doctor if you are suffering from kidney, liver, heart disease, or diabetes. Taking TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET during pregnancy may cause side effects like jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), unexplained bleeding, low blood sugar or an electrolyte imbalance in the newborn baby. Do not use the TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET if you cannot urinate, have low blood pressure (hypotension), and have a cardiogenic shock (sudden stopping blood flow to the heart). Reducing the amount of table salt (sodium chloride) in your food often relieves the body's swelling.
Uses of TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET
Medicinal Benefits Mweb
Key Benefits
TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET is a combination drug used to treat hypertension. When you take TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET , your body's blood vessels will be relaxed, and it will help lower the raised blood pressure. It also widens the blood vessels (lining of arteries wall) and improves blood flow. It helps in losing out excess fluids from the body by increasing the production of urine. This reduces the heart's workload and makes the heart more efficient at pumping blood throughout the body. Thus, it helps to lower high blood pressure, reducing the chances of heart attack or stroke. TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET also helps decrease fluid buildup, which reduces inflammation or swelling. In addition, this relieves Oedema and enables you to carry out your daily activities more efficiently.
Directions for Use
Side Effects of TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET
- Glucose intolerance (low or high level of glucose)
- Ankle swelling
- Sleepiness
- Headache (sense of heat in the face, ears, neck, and trunk)
- Flushing
- Tiredness
- Decreased potassium level in the blood
- Increased blood uric acid
- Altered blood lipid level
Drug Warnings
TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET should not be given to the people allergic to TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET , have low blood pressure (less than 90 mm of Hg), have had a heart attack, kidney disease, liver disease, gout (high uric acid), high cholesterol (hyperlipidemia), pregnant women or planning to get pregnant and breastfeeding women. Besides this, it is contraindicated in people with cardiogenic shock (sudden stopping of blood flow to the heart) and aortic stenosis (heart valve problem). TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET can pass into breast milk, but its effect on the baby is unknown. So, it is better to tell your doctor if you take TRILOSAR 12.5MG TABLET and breastfeeding. Tell your doctor if you are on low sodium (table salt) diet. Cases of electrolyte imbalance have been observed (like low levels of sodium, potassium, or magnesium in your blood). So your doctor might advise monitoring blood pressure, kidney function tests and electrolytes.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Using Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet together with dantrolene may increase the risk of hyperkalemia (high blood potassium).
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet with Dantrolene can cause an interaction, consult a doctor before taking it. You should seek medical attention if you experience nausea, vomiting, weakness, confusion, tingling of the hands and feet, a weak pulse, or a slow or irregular heartbeat. Do not stop using any medications without talking to a doctor.
Co-administration of Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet and cisapride may increase the risk or severity of an irregular heart rhythm that may be serious.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet with Cisapride is not recommended, please consult your doctor before taking it. Do not discontinue the medication without consulting a doctor.
Using Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet and mitotane together may drastically lower Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet blood levels, which makes the medicine less effective.
How to manage the interaction:
Although co-administration of Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet with mitotane can result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Using phenobarbital and Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet may drastically lower Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet blood levels, which makes the medicine less effective.
How to manage the interaction:
Although co-administration of phenobarbital with Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet can result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Coadministration of Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet and carbamazepine together may significantly reduce Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet blood levels, making the medicine less effective.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is an interaction between Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet with carbamazepine, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. However, if you experience any unusual symptoms contact the doctor immediately. Do not stop using any medications without talking to a doctor.
Using Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet and phenytoin together may drastically lower Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet blood levels, which makes the medicine less effective.
How to manage the interaction:
Although Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet with phenytoin can result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Using Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet and primidone together may lower Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet blood levels, which makes the medicine less effective.
How to manage the interaction:
Although co-administration of Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet with primidone can result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Coadministration of lemborexant and Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet may increase the blood levels of lemborexant.
How to manage the interaction:
Although co-administration of Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet with Lemborexant can result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. However, consult your doctor if you experience abnormal sleep patterns, worsening of depression, changes in heartbeat, or headache. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Taking simvastatin with Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet may result in considerably higher blood levels of simvastatin and may increase the risk of side effects (liver damage and rhabdomyolysis - an uncommon but serious illness characterized by the breakdown of skeletal muscle tissue).
How to manage the interaction:
Although taking Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet with simvastatin can result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. If you have unexplained muscular pain, soreness, or weakness while using simvastatin, especially if these symptoms are accompanied by fever or dark-colored urine, consult the doctor immediately. However, if you develop a fever, chills, joint pain or swelling, unusual bleeding or bruising, skin rash, itching, loss of appetite, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, dark colored urine, and/or yellowing of the skin or eyes, consult the doctor. Do not stop using any medications without a doctor's advice.
Co-administration of Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet can make Sirolimus may increase the risk of angioedema (a condition associated with swelling of the face, eyes, lips, tongue, throat, and occasionally also the hands and feet).
How to manage the interaction:
There may be a possibility of interaction between Trilosar 12.5mg Tablet and Sirolimus, but it can be taken if prescribed by a doctor. However, consult the doctor if you notice any swelling of the face, eyes, lips, tongue, throat, hands and feet or have trouble breathing or swallowing. Do not stop using any medications without a doctor's advice.
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List
- METOPROLOL
- RAMIPRIL
- HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE
- ATORVASTATIN
- SILDENAFIL
- CARBAMAZEPINE
- PHENOBARBITAL
- CYCLOSPORINE
- IBUPROFEN
- ASPIRIN
- RIFAMPICIN
- ZIPRASIDONE
- LITHIUM
Habit Forming
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Consume antioxidant-rich food. Blueberries, cherries, tomatoes, squash, and bell peppers are high in antioxidants.
- Eat natural diuretic foods. Asparagus, beets, green beans, grapes, onion, leafy greens, pineapple, leeks, pumpkin, and garlic are all-natural diuretic foods.
- Use healthy cooking oils like soybean, olive, canola, and coconut oil.
- You should avoid refined foods such as white bread, spaghetti, sugar, and red meat.
- Reduce or eliminate Trans fatty acids, which are found in commercially baked items such as cookies, cakes, crackers, French fries, onion rings, doughnuts, and processed foods.
- Avoid the consumption of too much salt or salty food.
- Keep your weight under control with a BMI of 19.5-24.9.
- Regular physical activity or exercise like walking improves your blood flow.
- When possible, elevate your legs or the swollen area on a chair or pillows.
- Avoid standing or sitting for extended periods of time.
- Avoid chronic stress, as it can raise your blood pressure.
- Spend time with your loved ones to cope with stress and practice mindfulness techniques.
- Quitting smoking and alcohol consumption is the best strategy to lower the risk of many health complications.
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
Out of StockTRILOSACAR TABLET
Zydus Cadila
₹35.45
(₹3.19 per unit)
70% CHEAPER

Have a query?
Buy best Cardiology products by
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Cipla Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Eris Life Sciences Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Lloyd Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
USV Pvt Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Elbrit Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
J B Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Alteus Biogenics Pvt Ltd
Hbc Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Fusion Health Care Pvt Ltd
Troikaa Pharmaceuticals Ltd
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Corona Remedies Pvt Ltd
Jubilant Lifesciences Ltd
Medley Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Knoll Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Msn Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Blue Cross Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Lividus Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Ranmarc Labs
Shrrishti Health Care Products Pvt Ltd
Sanofi India Ltd
Steris Healthcare
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Primus Remedies Pvt Ltd
Unison Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Eswar Therapeutics Pvt Ltd
Knoll Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Tas Med India Pvt Ltd
Systopic Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Indiabulls Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Sinsan Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Biochem Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Azkka Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Nirvana India Pvt Ltd
Orsim Pharma
Prevego Healthcare & Research Pvt Ltd
Econ Healthcare
Elinor Pharmaceuticals (P) Ltd
FDC Ltd
Sunij Pharma Pvt Ltd
Nicholas Piramal India Ltd
Astra Zeneca Pharma India Ltd
Pfizer Ltd
Lia Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Shine Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Elicad Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Indoco Remedies Ltd
Proqol Health Care Pvt Ltd
Vasu Organics Pvt Ltd
Biocon Ltd
Opsis Care Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Johnlee Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Merck Ltd
Wockhardt Ltd
Auspharma Pvt Ltd
Ergos Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Lakshya Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Ordain Health Care Global Pvt Ltd
Pficus De Med Pvt Ltd
ALICAN PHARMACEUTICAL PVT LTD
RPG Life Sciences Ltd
Glynis Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Orris Pharmaceuticals
Samarth Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Aprica Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Aretaeus Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Koye Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Neocardiab Care
Retra Life Science Pvt Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Alvio Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Arkas Pharma Pvt Ltd
Atos Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Divine Savior Pvt Ltd
Metalis Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Customers Also Bought




