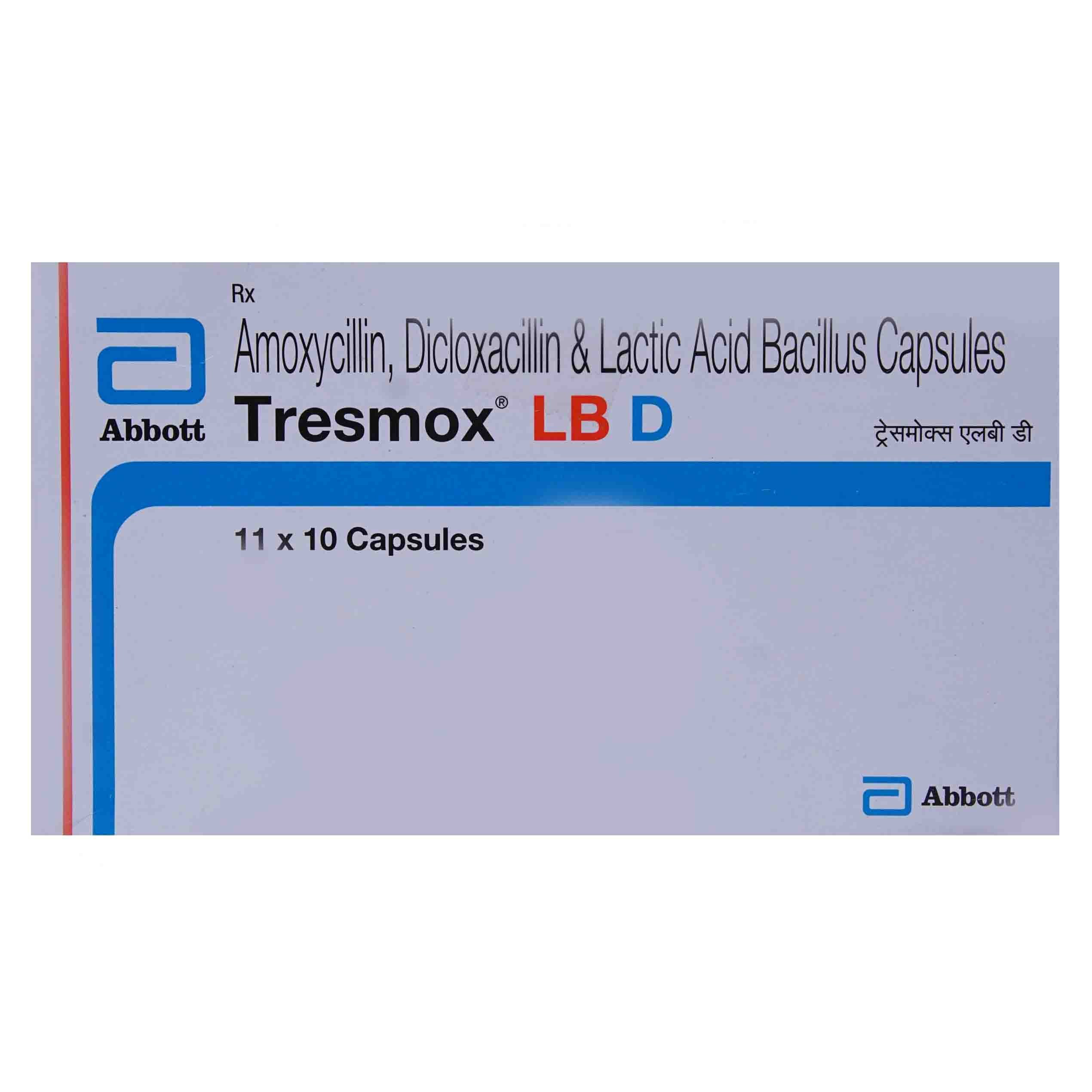
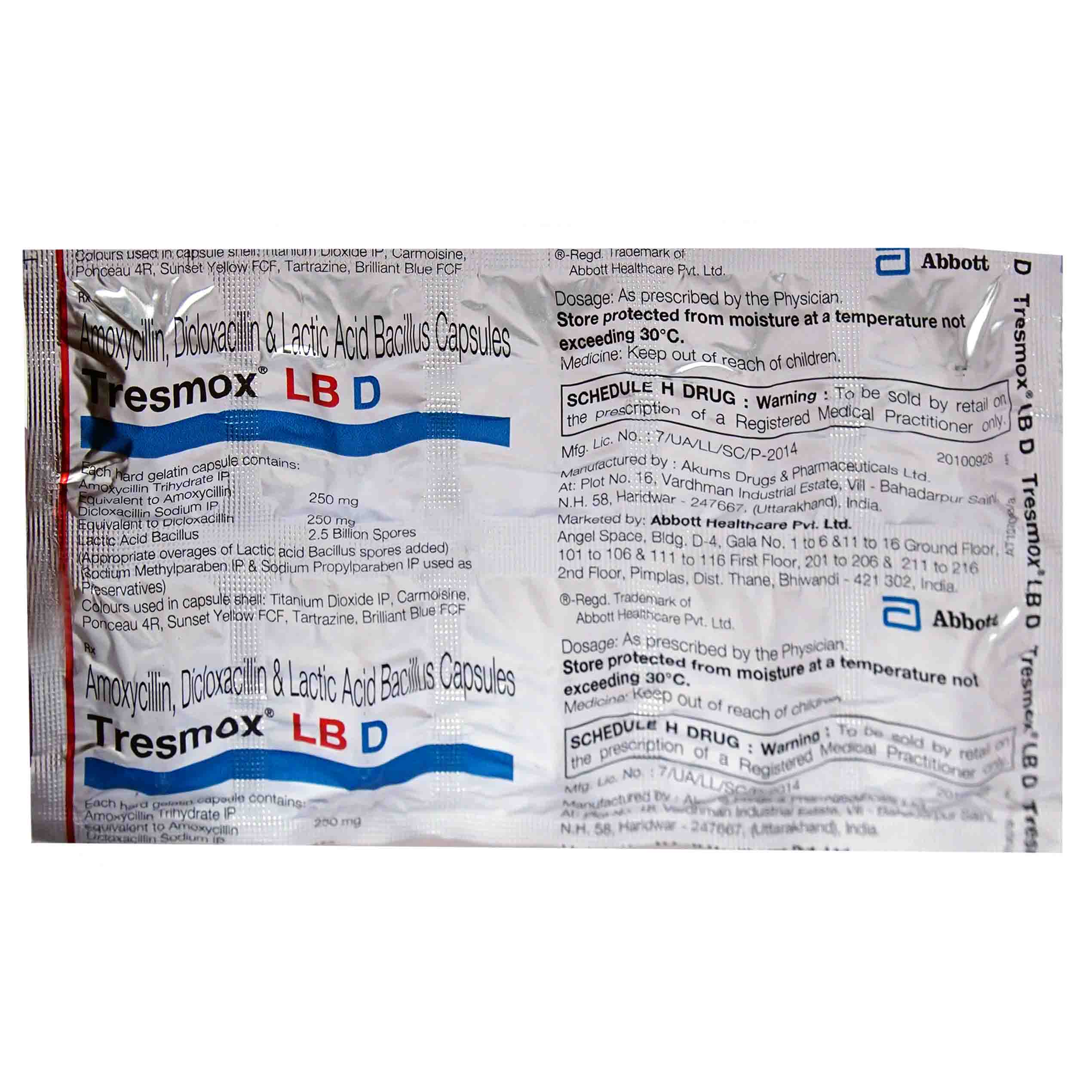
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Abbott India Ltd
Consume Type :
Oral
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :
Not Returnable
Disclaimer
While we strive to provide complete, accurate, and expert-reviewed content on our 'Platform', we make no warranties or representations and disclaim all responsibility and liability for the completeness, accuracy, or reliability of the aforementioned content. The content on our platform is for informative purposes only, and may not cover all clinical/non-clinical aspects. Reliance on any information and subsequent action or inaction is solely at the user's risk, and we do not assume any responsibility for the same. The content on the Platform should not be considered or used as a substitute for professional and qualified medical advice. Please consult your doctor for any query pertaining to medicines, tests and/or diseases, as we support, and do not replace the doctor-patient relationship.