R-Loc D Tablet

MRP ₹45
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹6.8 Cashback (15%)
know your delivery time
Provide Delivery Location
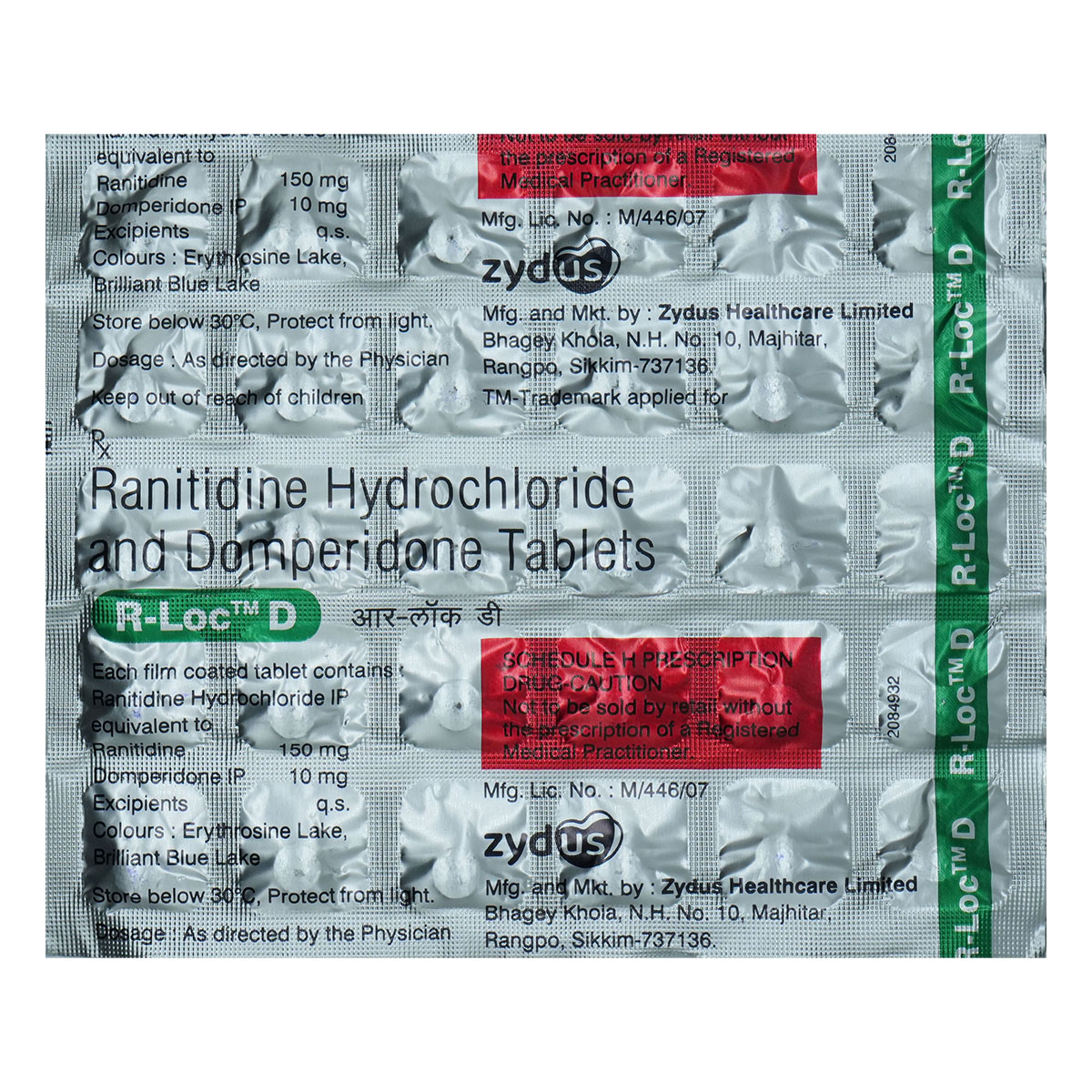
Composition :
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :
Selected Pack Size:30
30 ₹40.5
(₹1.35 per unit)
In Stock
15 ₹40.5
(₹2.7 per unit)
In Stock

Secure Payment

Trusted by 8 Crore Indians

Genuine Products
Therapeutic Class
Country of origin
Manufacturer/Marketer address
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
Disclaimer
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
Avoid consumption of alcohol while taking R-Loc D Tablet . Alcohol intake leads to increased production of stomach acid, thereby increases acidity and heartburn.
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
Consult your doctor before taking R-Loc D Tablet if you are pregnant; your doctor will prescribe only if the benefits outweigh the risks.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
Consult your doctor before taking R-Loc D Tablet ; your doctor will decide whether R-Loc D Tablet can be taken by breastfeeding mothers or not.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
R-Loc D Tablet may cause dizziness and sleepiness. Do not drive or operate machinery unless you are alert.
Liver
Consult your doctor
Dose adjustment may be needed. Consult your doctor before taking R-Loc D Tablet if you have a liver impairment or any concerns regarding this.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
Dose adjustment may be needed. Consult your doctor before taking R-Loc D Tablet if you have kidney impairment or any concerns regarding this.
Children
Safe if prescribed
R-Loc D Tablet should not be given to children as the safety and effectiveness were not established.
Product Substitutes
About R-Loc D Tablet
R-Loc D Tablet belongs to a group of medicines called gastrointestinal agents used to treat gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and peptic ulcers. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the food pipe (oesophagus). Peptic ulcers are sores that develop on the inner lining of the intestine and stomach.
R-Loc D Tablet is a combination of two drugs, namely: Ranitidine (H2 receptor antagonist) and Domperidone (a dopamine antagonist). Ranitidine works by blocking histamine H2 receptors located on the stomach lining, thereby reducing gastric acid secretion. Domperidone works by increasing the movements and contractions of stomach muscles. Together, R-Loc D Tablet helps in treating acidity.
You are advised to take R-Loc D Tablet for as long as your doctor has prescribed it for you depending on your medical condition. In some cases, you may experience certain common side-effects such as dry mouth, stomach pain, constipation, headache, sleepiness, and dizziness. Most of these side-effects do not require medical attention and will resolve gradually over time. However, you are advised to talk to your doctor if you experience these side-effects persistently.
Consult your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. R-Loc D Tablet may cause sleepiness and dizziness, so drive only if you are alert. R-Loc D Tablet should not be given to children as safety has not been established. Avoid consuming alcohol along with R-Loc D Tablet as it could lead to increased drowsiness and can elevate the production of stomach acid. Keep your doctor informed about all the medicines and your health condition to rule out any side-effects.
Uses of R-Loc D Tablet
Medicinal Benefits Mweb
Key Benefits
R-Loc D Tablet belongs to a group of medicines called gastrointestinal agents used to treat gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and peptic ulcers. R-Loc D Tablet is a combination of two drugs, namely: Ranitidine (H2 receptor antagonist) and Domperidone (a dopamine antagonist). Ranitidine works by blocking histamine H2 receptors located on the stomach lining, thereby reduces gastric acid secretion. Domperidone works by increasing the movements and contractions of stomach muscle. Together, R-Loc D Tablet helps in treating acidity.
Directions for Use
Side Effects of R-Loc D Tablet
- Dry mouth
- Stomach pain
- Constipation
- Headache
- Sleepiness
- Dizziness
Drug Warnings
Do not take R-Loc D Tablet if you are allergic to any of its contents. Inform your doctor before taking R-Loc D Tablet if you have a history of gastrointestinal bleeding, porphyria, or intestinal obstruction. R-Loc D Tablet may cause B12 deficiency in long-term treatment. Consult your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. R-Loc D Tablet may cause sleepiness and dizziness, so drive only if you are alert. R-Loc D Tablet should not be given to children as safety has not been established. Avoid consuming alcohol along with R-Loc D Tablet as it could lead to increased drowsiness and can elevate the production of stomach acid.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Co-administration of Domeperidone and Bepridil can increase the risk of irregular heart rhythm.
How to manage the interaction:
Although taking R-Loc D Tablet and Bepridil together can cause an interaction, it can be taken if your doctor has suggested it. If you experience lightheadedness, tiredness, increased heart rate, consult a doctor. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Combining Mizolastine with R-Loc D Tablet can increase the risk or severity of irregular heart rhythms.
How to manage the interaction:
Although taking R-Loc D Tablet and Mizolastine together can cause an interaction, it can be taken if your doctor has suggested it. However, if you experience sudden dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting, shortness of breath, chest pain or tightness, rapid heartbeat, contact a doctor immediately. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Coadministration of R-Loc D Tablet with Cisapride can increase the blood levels of R-Loc D Tablet.
How to manage the interaction:
There may be a possibility of interaction between R-Loc D Tablet and Cisapride, but it can be taken if prescribed by a doctor. In case you experience any side effects like swelling of the ankles or feet, unusual tiredness, redness, changes in menstrual ability, contact a doctor. It is recommended to do this to ensure your heart stays healthy. Do not stop using any medications without talking to a doctor.
Coadministration of R-Loc D Tablet with Halofantrine can Increase the risk of irregular heart rhythm.
How to manage the interaction:
Although taking R-Loc D Tablet and Halofantrine together can cause an interaction, it can be taken if your doctor has suggested it. If you experience lightheadedness, tiredness, increased heart rate, consult a doctor. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Coadministration of R-Loc D Tablet with Nefazodone can increase the blood levels of R-Loc D Tablet.
How to manage the interaction:
There may be a possibility of interaction between R-Loc D Tablet and Nefazodone, but it can be taken if prescribed by a doctor. In case you experience any side effects like swelling of the ankles or feet, unusual tiredness, redness, changes in menstrual ability, contact a doctor. It is recommended to do this to ensure your heart stays healthy. Do not stop using any medications without talking to a doctor.
Coadministration of R-Loc D Tablet with Toremifene can Increase the risk of irregular heart rhythm.
How to manage the interaction:
Although taking R-Loc D Tablet and Toremifene together can cause an interaction, it can be taken if your doctor has suggested it. If you experience lightheadedness, tiredness, increased heart rate, consult a doctor. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Coadministration of R-Loc D Tablet with Ketoconazole can Increase the risk of irregular heart rhythm.
How to manage the interaction:
Although taking R-Loc D Tablet and Ketoconazole together can cause an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has suggested it. If you experience lightheadedness, tiredness, increased heart rate, consult a doctor. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Coadministration of R-Loc D Tablet with Ritonavir can increase the blood levels of R-Loc D Tablet.
How to manage the interaction:
There may be a possibility of interaction between R-Loc D Tablet and Ritonavir, but it can be taken if prescribed by a doctor. In case you experience any side effects like swelling of the ankles or feet, unusual tiredness, redness, changes in menstrual ability, contact a doctor. It is recommended to do this to ensure your heart stays healthy. Do not stop using any medications without talking to a doctor.
Coadministration of R-Loc D Tablet with Clarithromycin can increase the risk of side effects.
How to manage the interaction:
There may be a possibility of interaction between R-Loc D Tablet and Clarithromycin, but it can be taken if prescribed by a doctor. Do not stop using any medications without talking to a doctor.
Coadministration of R-Loc D Tablet with Methadone can Increase the risk of irregular heart rhythm.
How to manage the interaction:
Although taking R-Loc D Tablet and Methadone together can cause an interaction, it can be taken if your doctor has suggested it. If you experience lightheadedness, tiredness, increased heart rate, consult a doctor. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List
- ACETAMINOPHEN
- NAPROXEN
- ASPIRIN
- IBUPROFEN
- METHADONE
- DULOXETINE
- CITALOPRAM
- ESCITALOPRAM
- CYANOCOBALAMIN
- KETOCONAZOLE
- FLUCONAZOLE
- VORICONAZOLE
- ERYTHROMYCIN
- CLARITHROMYCIN
- TELITHROMYCIN
- MOXIFLOXACIN
- PROPRANOLOL
- PROCAINAMIDE
- AMIODARONE
- DRONEDARONE
- QUINIDINE
- DISOPYRAMIDE
- DOFETILIDE
- SOTALOL
- DILTIAZEM
- VERAPAMIL
- HALOPERIDOL
- PIMOZIDE
- SERTINDOLE
- CISAPRIDE
- DOLASETRON
- MIZOLASTINE
- VANDETANIB
- DIAZEPAM
- PHENYTOIN
- THEOPHYLLINE
- WARFARIN
- GLIPIZIDE
- HALOFANTRINE
- TELAPREVIR
- TOREMIFENE
- VINCAMINE
- DIPHEMANIL
- MEQUITAZINE
Habit Forming
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Eat smaller meals more often.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption. Alcohol intake leads to increased production of stomach acid, thereby increases acidity and heartburn.
- Maintain a healthy weight by regular exercising.
- Avoid lying down after eating.
- Avoid tight-fitting clothes.
- Maintain a healthy weight by regular exercising.
- Practise relaxation techniques and avoid stress by doing yoga or meditation.
- Avoid foods such as high-fat food, spicy food, chocolates, citrus fruits, pineapple, tomato, onion, garlic, tea and soda.
- Avoid sitting continuously as it may trigger acidity. Take a break of 5 minutes every hour by doing brisk walking or stretching.
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
Out of StockGertac DM Tablet
Zydus Cadila
₹6.12
(₹0.55 per unit)
59% CHEAPERRX
Out of StockAztec D 10mg/150mg Tablet
Ind Swift Laboratories Ltd
₹6.25
(₹0.56 per unit)
58% CHEAPERRX
Out of StockHelkoss D 10mg/150mg Tablet
Lupin Ltd
₹6.5
(₹0.59 per unit)
56% CHEAPER

Have a query?
Buy best Gastro Enterology products by
Abbott India Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
Cipla Ltd
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Wallace Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
J B Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Fourrts India Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd
FDC Ltd
Eris Life Sciences Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Medishri Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Medley Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Tas Med India Pvt Ltd
Signova Pharma
Tablets India Ltd
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Wockhardt Ltd
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Sanatra Healthcare Ltd
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Blue Cross Laboratories Pvt Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
Hetero Drugs Ltd
Indoco Remedies Ltd
Vasu Organics Pvt Ltd
Biological E Ltd
Primus Remedies Pvt Ltd
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Corona Remedies Pvt Ltd
Pfizer Ltd
Albert David Ltd
DR Johns Lab Pharma Pvt Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Ordain Health Care Global Pvt Ltd
Systopic Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Ozone Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Foregen Healthcare Ltd
Medgen Drugs And Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Panacea Biotec Ltd
Samarth Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Shine Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Adonis Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Dey's Medical Stores (Mfg) Ltd
Eskag Pharma Pvt Ltd
Hetero Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Indchemie Health Specialities Pvt Ltd
Meyer Organics Pvt Ltd
RPG Life Sciences Ltd
Troikaa Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Biochem Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Shreya Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Sinsan Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
3M India Ltd
Chemo Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Levin Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Meridian Enterprises Pvt Ltd
Overseas Health Care Pvt Ltd
Saf Fermion Ltd
Sanzyme Pvt Ltd
Steris Healthcare
USV Pvt Ltd
Seagull Pharmaceutical Pvt Ltd
Votary Laboratories (India) Ltd
Win Medicare Ltd
Yuventis Pharmaceuticals
Aar Ess Remedies Pvt Ltd
Caplet India Pvt Ltd
Piramal Enterprises Ltd
Sanofi India Ltd
Cnx Health Care Pvt Ltd
Galpha Laboratories Ltd
Intra Labs India Pvt Ltd
Kinesis Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Msn Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Olcare Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Rapross Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Ronyd Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Saffron Therapeutics Pvt Ltd
Solariz Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Syndicate Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Aurz Pharmaceutical Pvt Ltd
Biophar Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Frequently Bought Together
Customers Also Bought

_0.jpg?tr=q-85)


















