Lupitrin-P Tablet

MRP ₹179
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹26.9 Cashback (15%)
know your delivery time
Provide Delivery Location
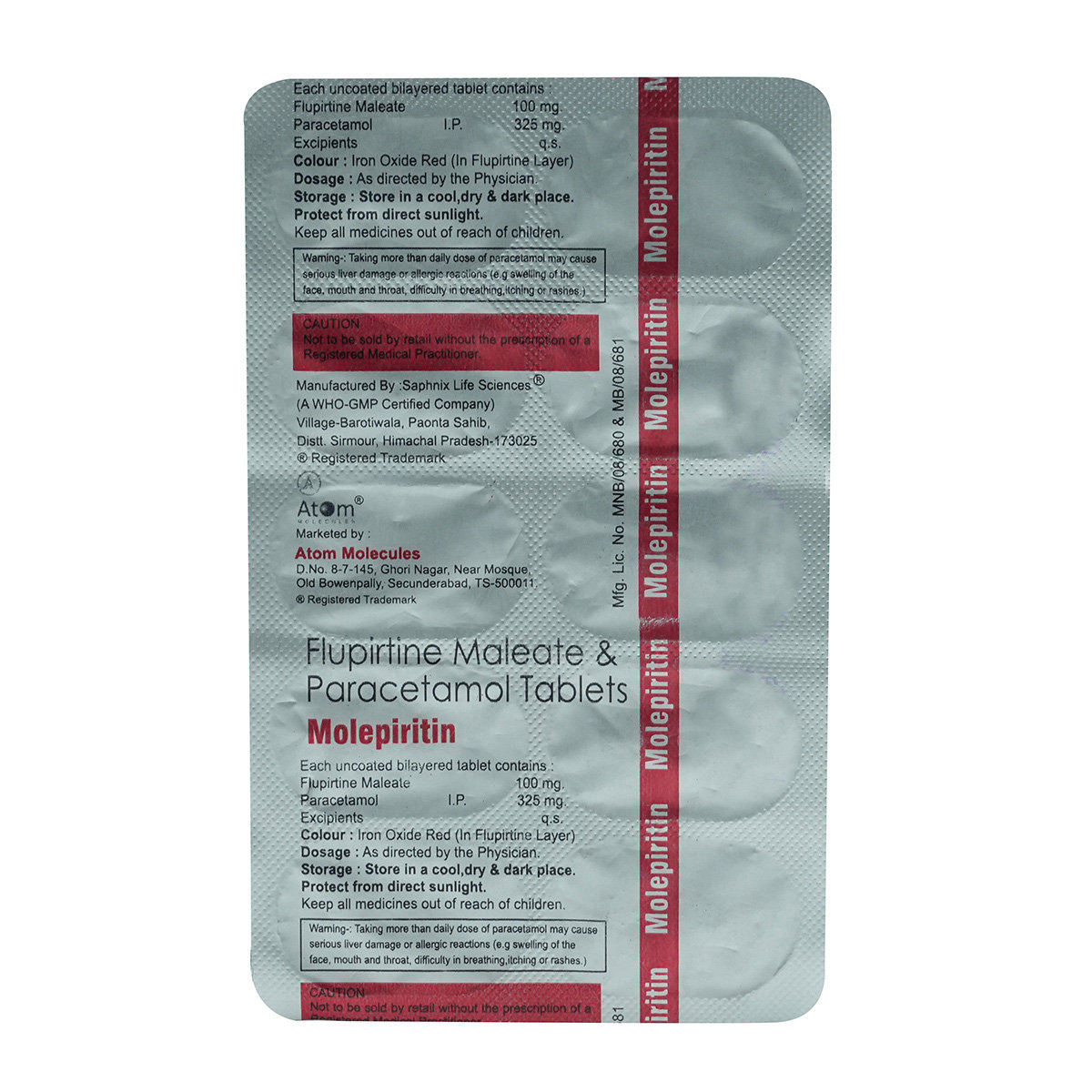
Composition :
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :

Secure Payment

Trusted by 8 Crore Indians

Genuine Products
Therapeutic Class
Country of origin
Manufacturer/Marketer address
Disclaimer
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
Consuming alcohol with Lupitrin-P Tablet is not advisable as it may cause unpleasant side effects, or you may become more sensitive to the effects of alcohol.
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
Lupitrin-P Tablet is not recommended during pregnancy. However, your doctor may prescribe it for you during pregnancy if he/she feels the benefit outweighs the risk.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
According to the studies available to date, a small percentage of flupirtine maleate passes into breast milk. Therefore, flupirtine maleate must not be administered during lactation unless necessary.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
Avoid driving or operating heavy machinery after taking Lupitrin-P Tablet , as it may cause dizziness.
Liver
Consult your doctor
Lupitrin-P Tablet can cause liver toxicity. So, it should be avoided in patients with liver diseases. However, dose adjustments and close monitoring are necessary if it is used in patients with liver diseases.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
In patients with kidney problems, dose adjustments of Lupitrin-P Tablet are required. Therefore, use Lupitrin-P Tablet only when prescribed by a doctor.
Children
Safe if prescribed
It is recommended to consult a doctor before using Lupitrin-P Tablet in children below six years.
Product Substitutes
Reference
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3339720/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3557425/#:~:text=Adverse%20events%20commonly%20reported%20were,%2C%20depression%2C%20disorientation%20and%20hallucinations.
- https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/files/pil.5916.pdf
- http://mri.cts-mrp.eu/download/DE_H_3430_001_FinalSPC_2of2.pdf
- https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/restrictions-use-flupirtine-containing-medicines-cmdh-endorses-prac-recommendation#:~:text=Flupirtine%20is%20a%20non%2Dopioid,following%20orthopaedic%20surgery%20or%20injuries.
About Lupitrin-P Tablet
Lupitrin-P Tablet is a combination medication that belongs to the analgesic medication class. It is widely used in the treatment of acute and chronic pain, fever, headache, joint pains, dysmenorrhea (period pain), postoperative pain, toothache after dental extraction, and myalgia (muscle pain). Pain is a widely used term used to describe an unpleasant feeling or discomfort. It ranges from mild to severe. The severity of the pain depends on the underlying condition. Inflammation is the immune system's natural response to injury or infection.
Lupitrin-P Tablet contains flupirtine and paracetamol. Flupirtine is an analgesic (non-opioid analgesic) which works by blocking the transmission of pain signals to the brain to lower pain perception. Paracetamol is an analgesic (pain reliever) and an antipyretic (fever reducer), which works by blocking the release of certain chemical messengers that cause fever and pain. Thus Lupitrin-P Tablet alleviates pain and other associate conditions.
Use Lupitrin-P Tablet as directed by the physician only. The dose and duration of the medication depend on your condition and its severity. The common side effects of Lupitrin-P Tablet include nausea, vomiting, wind, abdominal discomfort, diarrhoea, constipation, heartburn, drowsiness, dizziness, headache, and depression. Most of these side effects of Lupitrin-P Tablet are temporary, do not require medical attention, and gradually resolve over time. However, if the side effects are persistent, reach out to your doctor.
Before taking Lupitrin-P Tablet , inform your doctor if you are allergic to flupirtine, paracetamol, or other ingredients. Besides, inform your doctor if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have any pre-existing conditions such as liver diseases such as hepatic encephalopathy (loss of brain function due to liver damage), chronic alcoholism, or cholestasis (reduced bile flow), renal impairment, myasthenia gravis (chronic neuromuscular disease), or heart diseases. If Lupitrin-P Tablet is given in patients with liver diseases, liver function should be monitored closely. Lupitrin-P Tablet causes drowsiness and dizziness, so drive only if you are alert. Lupitrin-P Tablet is not recommended for children younger than six years old.
Uses of Lupitrin-P Tablet
Medicinal Benefits Mweb
Key Benefits
Lupitrin-P Tablet contains flupirtine (non-opioid analgesic) and paracetamol (analgesic and antipyretic). Flupirtine works by blocking the glutamate receptors that are involved in producing pain signals. It also has muscle relaxant properties. Paracetamol acts as an analgesic and antipyretic by inhibiting the release of prostaglandins (chemical mediators) that cause pain, inflammation, and fever. Altogether provide relief from pain and associated symptoms.
Directions for Use
Side Effects of Lupitrin-P Tablet
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Colic/wind
- Gastric
- Abdominal discomfort
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Heartburn
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Depression
Drug Warnings
Avoid using Lupitrin-P Tablet if you are allergic to analgesics or painkillers. People with liver diseases, kidney diseases, and elderly people above 65 years of age may require dose adjustments. If Lupitrin-P Tablet is given to patients with liver impairment, liver function should be closely monitored. It is advised to discontinue use if you notice any signs of liver damage such as nausea, vomiting, yellowed skin and eyes (jaundice), abdominal pain, loss of appetite, itchy skin, and dark-coloured urine, etc.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Co-administration of Lupitrin-P Tablet may decrease the excretion rate of Oxazepam which could result in a higher serum level.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction between Oxazepam and Lupitrin-P Tablet, you can take these medicines together if prescribed by a doctor. Do not stop using any medications without a doctor's advice.
Co-administration of ketamine and Lupitrin-P Tablet may decrease the effectiveness of Ketamine which could result in a higher blood level.
How to manage the interaction:
Although taking Ketamine and Lupitrin-P Tablet together can evidently cause an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has suggested it. If you're feeling very sleepy or having trouble breathing, it's important to contact your doctor right away. Do not stop using any medications without a doctor's advice.
Co-administration of Teriflunomide with Lupitrin-P Tablet may increase the risk or severity of Liver problems.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Lupitrin-P Tablet with Teriflunomide together can possibly result in an interaction, but it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Co-administration of Lupitrin-P Tablet and Ketoconazole may increase the risk of liver injury.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction between Lupitrin-P Tablet and Ketoconazole, you can take these medicines together if prescribed by a doctor. However, if you have joint pain or swelling, fever, chills, unusual bleeding or bruising, skin rash, itching, over-tiredness, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, stomach pain, dark-colored urine, light-colored stools, and/or yellowing of the skin or eyes, contact a doctor immediately as these may be signs and symptoms of liver damage. Do not discontinue the medication without consulting a doctor.
Co-administration of Lupitrin-P Tablet and Leflunomide may increase the risk of liver problems.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction between Lupitrin-P Tablet and Leflunomide, they can be taken together if prescribed by a doctor. However, if you experience fever, chills, joint pain or swelling, unusual bleeding or bruising, skin rash, itching, less desire to eat, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or yellowing of the skin or eyes, contact a doctor immediately. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Co-administration of Lupitrin-P Tablet and Valdecoxib may increase the risk or severity of adverse effects.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction between Lupitrin-P Tablet and Valdecoxib, you can take these medicines together if prescribed by a doctor. However, if the side effects worsen, please consult a doctor.
Co-administration of Lomitapide and Lupitrin-P Tablet may increase the risk of severity of liver injury.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction between Lupitrin-P Tablet and Lomitapide, you can take these medicines together if prescribed by a doctor. Do not stop using any medications without a doctor's advice.
Co-administration of Mipomersen with Lupitrin-P Tablet may increase the risk or severity of liver injury.
How to manage the interaction:
There may be a possibility of interaction between Lupitrin-P Tablet and Mipomersen, but it can be taken if prescribed by a doctor. Do not stop using any medications without talking to a doctor.
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List
- WARFARIN
Habit Forming
Special Advise
- Flupirtine may interact with anticoagulants such as warfarin. A blood test called the PT is needed to monitor this potential interaction.
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Do not take alcohol.
- Include more glucosamine, chondroitin sulphate, vitamin D, and calcium-enriched supplements. Besides this, turmeric and fish oils can help reduce inflammation in the tissue.
- Please do not go for heavy exercise as it may increase your joint pain in arthritis. Instead, you can do stretching, low impact aerobic exercises like walking on a treadmill, bike riding and swimming. You can also strengthen your muscles by lifting light weights.
- In the chronic condition of arthritis or joint pain, try to include fish like salmon, trout, tuna, and sardines. These fishes are enriched with omega-3 fatty acids that minimum level of chemical called cytokines, which ramp up inflammation.
- Your sitting posture is important, especially when you have pain and inflammation. Try to sit as little as possible and only for a short time. Long-term immobility is harmful in conditions like arthritis. Use back support like a rolled-up towel to minimise pain at the back of your spine curve. Keep your knees and hips at a right angle. Besides this, you can also use a footrest if required.
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
Flupiwell-P Tab 10'S
Primus Remedies Pvt Ltd
₹133.5
(₹12.02 per unit)
25% CHEAPERRX
Apyridine-P Tablet 10's
Primus Remedies Pvt Ltd
₹133.5
(₹12.02 per unit)
25% CHEAPERRX
Exotin P Tablet 10's
Galaxus Pharmaceuticals
₹145
(₹13.05 per unit)
18% CHEAPER

Have a query?
Buy best C.n.s Drugs products by
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Cipla Ltd
Alteus Biogenics Pvt Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
D D Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Icon Life Sciences
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Tripada Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Arinna Lifesciences Ltd
Linux Laboratories Pvt Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Talent India Pvt Ltd
Tas Med India Pvt Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Cnx Health Care Pvt Ltd
Eris Life Sciences Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Sigmund Promedica
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Troikaa Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Consern Pharma Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Shine Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Wockhardt Ltd
Ardent Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Crescent Formulations Pvt Ltd
Theo Pharma Pvt Ltd
Reliance Formulation Pvt Ltd
Ikon Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Propel Healthcare
Neon Laboratories Ltd
Jagsam Pharma
Msn Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Pulse Pharmaceuticals
Sanofi India Ltd
Med Manor Organics Pvt Ltd
Hetero Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Novartis India Ltd
Crescent Therapeutics Ltd
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Solvate Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Mova Pharmaceutical Pvt Ltd
Psyco Remedies Ltd
Tripada Lifecare Pvt Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Cyrus Remedies Pvt Ltd
Medishri Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Matteo Health Care Pvt Ltd
Hbc Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Lyf Healthcare
Matias Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Mesmer Pharmaceuticals
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Capital Pharma
Crescent Pharmaceuticals
Medopharm Pvt Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Kivi Labs Ltd
Talin Remedies Pvt Ltd
USV Pvt Ltd
Quince Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Solis Pharmaceuticals
Infivis Life Care
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Pfizer Ltd
Wallace Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
A N Pharmacia Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Blue Cross Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Jenburkt Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Lia Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Mano Pharma
Medley Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Primus Remedies Pvt Ltd
FDC Ltd
Maneesh Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Apex Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Gagnant Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Ozone Pharmaceuticals Ltd
RPG Life Sciences Ltd
Strides Shasun Ltd
Unichem International
GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Kuresys Labs Pvt Ltd
LA Pharma
Trion Pharma India Llp