Lori Injection 2 ml


MRP ₹11.5
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹1.1 Cashback (10%)
know your delivery time
Provide Delivery Location

Secure Payment

Trusted by 8 Crore Indians

Genuine Products
Therapeutic Class
Country of origin
Manufacturer/Marketer address
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
Disclaimer
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
Intake of alcohol can increase the side effects of Lori Injection 2 ml, like dizziness, drowsiness, and difficulty concentrating. In a few cases, people may also experience impaired thinking and judgment. Hence, avoid consuming alcohol while being treated with Lori Injection 2 ml.
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
Lori Injection 2 ml is recommended in pregnancy if clearly necessary, Inform your doctor if you are pregnant or suspect pregnancy. Your doctor will weigh the benefits and potential risks before prescribing Lori Injection 2 ml.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
Lori Injection 2 ml may not be recommended in breastfeeding as it may harm your infant. Inform your doctor if you are breastfeeding. Your doctor will weigh the benefits and potential risks before prescribing Lori Injection 2 ml.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
Lori Injection 2 ml may cause a reduction in mental awareness, affect concentration and may cause dizziness. Hence, avoid driving after receiving Lori Injection 2 ml.
Liver
Consult your doctor
Lori Injection 2 ml is not recommended for use in people with severe liver disease. Inform your doctor if you have a history of liver disease or an ongoing liver problem. Your doctor may adjust the dose of Lori Injection 2 ml if necessary.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
Inform your doctor if you have kidney problems or a history of kidney disease. Your doctor may adjust your dose depending upon your kidney condition.
Children
Safe if prescribed
The safety and effectiveness of Lori Injection 2 ml in neonates (30 days or less) have not been established. Your paediatrician will recommend this medicine based on the condition of your child.
Product Substitutes
About Lori Injection 2 ml
Lori Injection 2 ml belongs to a group of medications called benzodiazepine used to treat anxiety, muscle spasms, and epilepsy/seizures/fits. It can also be used as a sedative during surgery or dental procedure. Besides this, it is also used to manage alcohol withdrawal symptoms like agitation, tremor, or hallucinations. An anxiety disorder is a mental condition characterized by feelings of excessive fear or worry that affect an individual's daily activities.
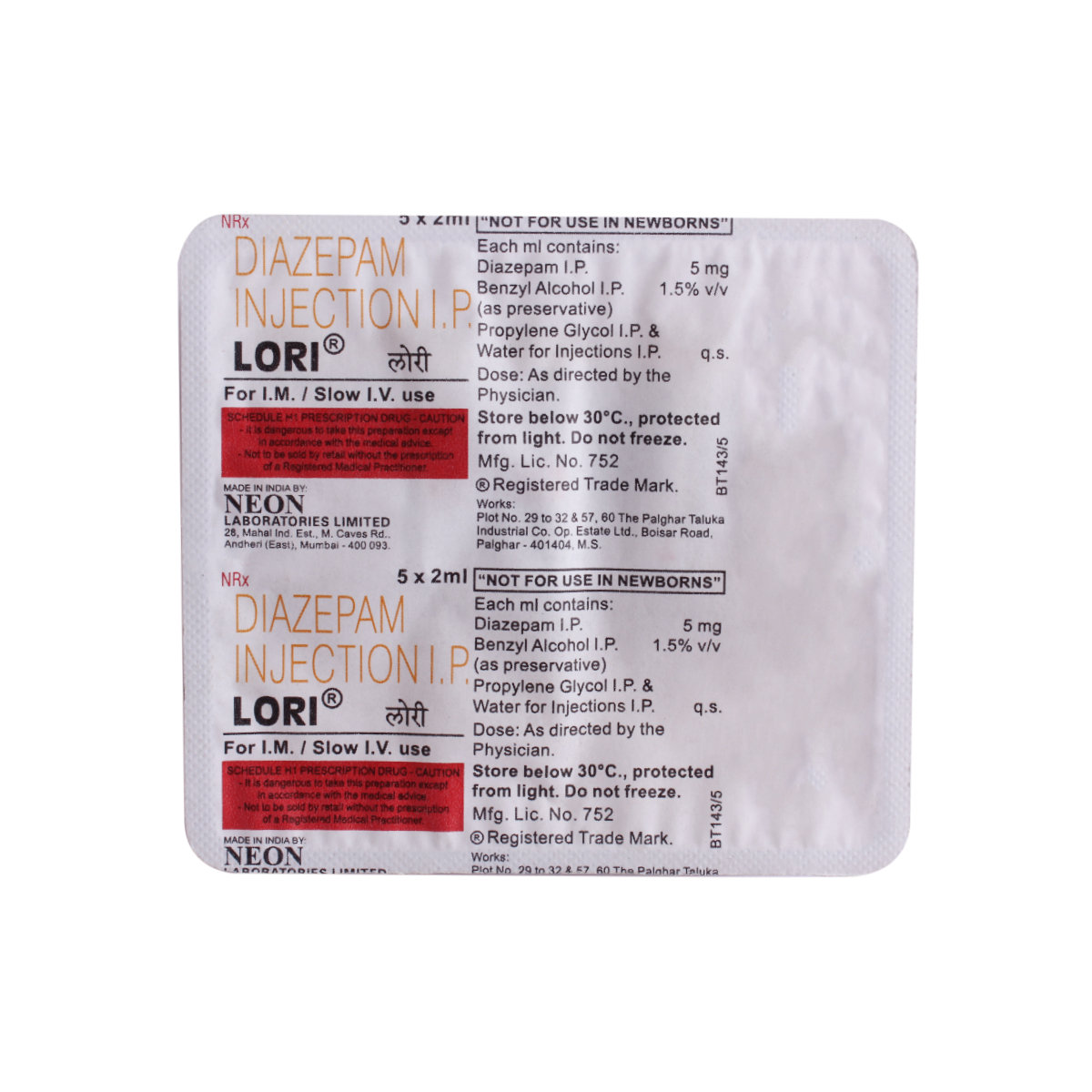
Lori Injection 2 ml contains diazepam, which works by increasing levels of the calming chemical mediator known as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain; this helps relieve anxiety, stops seizure attacks (fits) and relaxes the tense muscles.
Lori Injection 2 ml will be administered by a healthcare professional; do not self-administer. Sometimes, Lori Injection 2 ml may cause side effects, such as drowsiness, fatigue, confusion, unsteadiness, or dizziness. Most of these side effects of Lori Injection 2 ml do not require medical attention and gradually resolve over time. However, if the side effects are persistent, reach out to your doctor.
Inform your doctor if you have lung disease, muscle weakness (myasthenia gravis), sleeping disorder, severe liver disease, or problems with alcohol consumption or other prescription recreational drugs. Inform your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Do not drive or operate machinery as Lori Injection 2 ml may reduce mental alertness. It is advisable to avoid alcohol after taking this medicine to prevent adverse effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and difficulty concentrating.
Uses of Lori Injection 2 ml
Medicinal Benefits Mweb
Key Benefits
Lori Injection 2 ml belongs to a group of medications called benzodiazepine used to treat anxiety, muscle spasms, and epilepsy/seizures/fits. It can also be used as a sedative during surgery or dental procedure. Besides this, it is also used to manage alcohol withdrawal symptoms like agitation, tremor, or hallucinations. Lori Injection 2 ml contains diazepam, which works by increasing levels of the calming chemical mediator known as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain; this helps relieve anxiety, stops seizure attacks (fits) and relaxes the tense muscles.
Directions for Use
Side Effects of Lori Injection 2 ml
- Drowsiness
- Feeling sleepy (sedation)
- Light-headedness
- Unsteadiness, or dizziness
- Confusion
Drug Warnings
Lori Injection 2 ml is not recommended for people with hypersensitivity to diazepam, other related benzodiazepines or any components present in Lori Injection 2 ml, people with a phobia (a fear of a particular object or situation), difficulty breathing, porphyria (a disorder of the blood brought on by a buildup of specific substances connected to the proteins in red blood cells), liver impairment, muscle weakness (myasthenia gravis), open-angle glaucoma or acute narrow-angle glaucoma unless patients are receiving appropriate therapy. Inform your doctor if you have suicidal thoughts, difficulty concentrating, sleep disorders, depression, breathing problems, history of alcohol/drug abuse, arteriosclerosis (narrowing of the blood vessels), lung, kidney, liver or heart problems. Concomitant use of opioids and benzodiazepines may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Taking of Lori Injection 2 ml with methadone may cause serious side effects like respiratory distress.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction, Lori Injection 2 ml should be taken with methadone only if prescribed by the doctor. The doctor may prescribe alternatives that do not interact, dose adjustment, or more frequent monitoring to safely use both medications. Do not discontinue the medication without consulting a doctor.
Co-administration of Tapentadol together with Lori Injection 2 ml can increase the risk or severity of side effects like decreased breathing rate, irregular heart rhythms, or problems with movement and memory.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Lori Injection 2 ml with Tapentadol can result in an interaction, it can be taken if your doctor has advised it. Contact a doctor immediately if you experience signs such as drowsiness, lightheadedness, palpitations, confusion, severe weakness, or difficulty breathing. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Co-administration of Lori Injection 2 ml with esketamine may increase side effects such as confusion, drowsiness, difficulty concentrating, and impairment in thinking, judgment, reaction speed, and motor coordination.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction, Lori Injection 2 ml should be taken with esketamine if prescribed by the doctor. However, avoid driving or operating heavy machinery after treatment with esketamine as you may experience drowsiness. Do not discontinue the medication without consulting a doctor.
Taking Lori Injection 2 ml together with fluvoxamine may cause an increase in side effects such as drowsiness, confusion, muscle weakness, and fainting.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction, Lori Injection 2 ml can be taken with fluvoxamine if prescribed by the doctor. However, if you experience any unusual symptoms consult your doctor. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Co-administration of Sufentanil with Lori Injection 2 ml can increase the risk of adverse effects.
How to manage the interaction:
Co-administration of Lori Injection 2 ml with Sufentanil can possibly result in an interaction, but it can be taken if your doctor has advised it. If you notice any of these symptoms - feeling tired or sleepy, having trouble breathing, or a slower heartbeat - make sure to contact your doctor right away. Do not stop using any medications without first talking to your doctor.
Co-administration of Lori Injection 2 ml with clozapine may increase the effects of both medicines.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction, Lori Injection 2 ml can be taken with clozapine if prescribed by the doctor. Consult the prescriber if you experience side effects like low blood pressure, confusion, drowsiness, shallow breathing, incoordination, and weak pulse. Your doctor may advise dose adjustment or frequent monitoring to safely use both medicines. Do not discontinue the medications without consulting a doctor.
Taking of Lori Injection 2 ml with hydromorphone may cause serious side effects like respiratory depression.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction, Lori Injection 2 ml should be taken with hydromorphone only if prescribed by the doctor. Consult the doctor if you have any concerns, doctor may prescribe alternatives that do not interact. Do not discontinue the medication without consulting a doctor.
Co-administration of Lori Injection 2 ml with oxycodone may cause serious side effects like respiratory distress.
How to manage the interaction:
Consult the doctor if you are taking Lori Injection 2 ml and oxycodone. The doctor may prescribe alternatives that do not interact, or dose adjustment, or frequent monitoring to safely use both medicines. Do not discontinue the medication without consulting a doctor.
Co-administration of Lori Injection 2 ml with Ketamine can increase the risk of CNS depression.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Ketamine with Lori Injection 2 ml together can possibly result in an interaction, but it can be taken if your doctor has advised it. If you feel dizzy, sleepy, confused, have trouble focusing, feel too relaxed, or have trouble breathing, make sure to contact your doctor right away. Do not stop using any medications without first talking to your doctor.
Co-administration of Lori Injection 2 ml with tramadol may cause serious side effects like respiratory distress or coma.
How to manage the interaction:
Consult the doctor if you are taking Lori Injection 2 ml and tramadol. The doctor may prescribe alternatives that do not interact, dose adjustment, or more frequent monitoring to safely use both medications. Do not discontinue the medication without consulting a doctor.
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Lori Injection 2 ml shouldn't be used by people with myasthenia gravis.
How to manage the interaction:
The use of Lori Injection 2 ml is not recommended in patients with myasthenia gravis (an autoimmune disease).
Injecting benzodiazepines into individuals who are in shock or a coma is not advised. In these patients, the hypnotic and hypotensive effects of these drugs may last longer and be more potent.
How to manage the interaction:
The hypnotic (sleep-inducing) and hypotensive (lowering blood pressure) effects of these agents may be prolonged and intensified. The medicine should not be administered to patients in shock or coma.
The incidence of generalised tonic-clonic seizures (grand mal) or their onset may be accelerated in people with seizure disorders who use benzodiazepines.
How to manage the interaction:
Benzodiazepines may increase the occurrence of seizures. Dose adjustment or initiation of appropriate anticonvulsant medication may be needed. Do not discontinue medication without first consulting with the physician.
When administered in large doses and/or by intravenous administration, benzodiazepines have the potential to cause respiratory depression and apnea.
How to manage the interaction:
Usually when given in high dosages and/or by intravenous administration, benzodiazepines may cause respiratory depression and apnea. Therapy with benzodiazepines should be administered cautiously in these patients.
The liver breaks down benzodiazepines, and the metabolites are then eliminated in the urine. The oxidative N-dealkylation of chlordiazepoxide, clorazepate, Lori Injection 2 ml, flurazepam, and quazepam results in active metabolites that have significantly longer half-lives than the parent substance.
How to manage the interaction:
Benzodiazepines are metabolized by the liver. Therapy with benzodiazepines should be administered cautiously at lower initial dosages in patients with impaired liver function.
It is possible for benzodiazepines to lead to abuse and dependence. Particularly with repeated usage and/or high dosages, tolerance and physical and psychological dependence may develop.
How to manage the interaction:
Benzodiazepines have the potential to cause dependence and abuse. It should be used with caution in patients with addiction- prone individuals, such as those with a history of alcohol or substance abuse. The dose should be gradually reduced if dependency is suspected.
The makers believe that using benzodiazepines while a patient has acute angle-closure glaucoma or untreated open-angle glaucoma is contraindicated.
How to manage the interaction:
Benzodiazepine is not recommended in patients with acute angle-closure glaucoma or untreated open-angle glaucoma.
Alcohol and benzodiazepines should not be combined. Vital signs are decreased in alcohol-intoxicated patients.
How to manage the interaction:
The use of benzodiazepines with alcohol is not recommended. Therapy with benzodiazepines should be administered cautiously in patients who might be prone to acute alcohol intake.
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List
- FLUOXETINE
- CLOZAPINE
- CETIRIZINE
- ERYTHROMYCIN
- SUXAMETHONIUM
- TUBOCURARINE
- MORPHINE
- PHENOBARBITAL
- HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE
- HYDRALAZINE
- CIMETIDINE
- OMEPRAZOLE
- CARBAMAZEPINE
- PRIMIDONE
- AMPRENAVIR
- RITONAVIR
- LEVODOPA
- KETAMINE
- THEOPHYLLINE
- LOFEXIDINE
- NABILONE
- RIFAMPICIN
- DISULFIRAM
- PHENYTOIN
Habit Forming
Special Advise
- The use of Lori Injection 2 ml may increase the risk of misuse, abuse, and addiction. Therefore, before prescribing Lori Injection 2 ml and throughout the treatment, the patient's risk for misuse, abuse, and addiction should be assessed.
- Lori Injection 2 ml may cause withdrawal symptoms if treatment is stopped suddenly. Therefore, the dose should be gradually reduced to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Yoga, meditation, mindfulness-based cognitive therapy, and mindfulness-based stress reduction can help improve your mindfulness.
- De-stress by meditating, reading books, taking a nice bubble bath, or listening to relaxing music.
- Regular exercise can help reduce anxiety by generating endorphins and enhancing your sleep and self-image.
- Drink plenty of water to keep hydrated.
- Include a diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, and fruits.
- Limit your consumption of alcohol, coffee, added sugar, salt, and fat.
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
Out of StockNot for online saleTanpose Injection 2 ml
Tamman Titoe Pharma Pvt Ltd
₹11.06
(₹5.53/ 1ml)
6% COSTLIER

Have a query?
Buy best C.n.s Drugs products by
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Cipla Ltd
Alteus Biogenics Pvt Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
D D Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Icon Life Sciences
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Tripada Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Arinna Lifesciences Ltd
Linux Laboratories Pvt Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Talent India Pvt Ltd
Tas Med India Pvt Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Cnx Health Care Pvt Ltd
Eris Life Sciences Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Sigmund Promedica
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Troikaa Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Consern Pharma Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Shine Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Wockhardt Ltd
Ardent Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Crescent Formulations Pvt Ltd
Theo Pharma Pvt Ltd
Reliance Formulation Pvt Ltd
Ikon Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Propel Healthcare
Neon Laboratories Ltd
Jagsam Pharma
Msn Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Pulse Pharmaceuticals
Sanofi India Ltd
Med Manor Organics Pvt Ltd
Hetero Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Novartis India Ltd
Crescent Therapeutics Ltd
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Solvate Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Mova Pharmaceutical Pvt Ltd
Psyco Remedies Ltd
Tripada Lifecare Pvt Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Cyrus Remedies Pvt Ltd
Medishri Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Matteo Health Care Pvt Ltd
Hbc Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Lyf Healthcare
Matias Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Mesmer Pharmaceuticals
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Capital Pharma
Crescent Pharmaceuticals
Medopharm Pvt Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Kivi Labs Ltd
Talin Remedies Pvt Ltd
USV Pvt Ltd
Quince Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Solis Pharmaceuticals
Infivis Life Care
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Pfizer Ltd
Wallace Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
A N Pharmacia Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Blue Cross Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Jenburkt Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Lia Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Mano Pharma
Medley Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Primus Remedies Pvt Ltd
FDC Ltd
Maneesh Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Apex Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Gagnant Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Ozone Pharmaceuticals Ltd
RPG Life Sciences Ltd
Strides Shasun Ltd
Unichem International
GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Kuresys Labs Pvt Ltd
LA Pharma
Trion Pharma India Llp


_0.jpg?tr=q-85)

