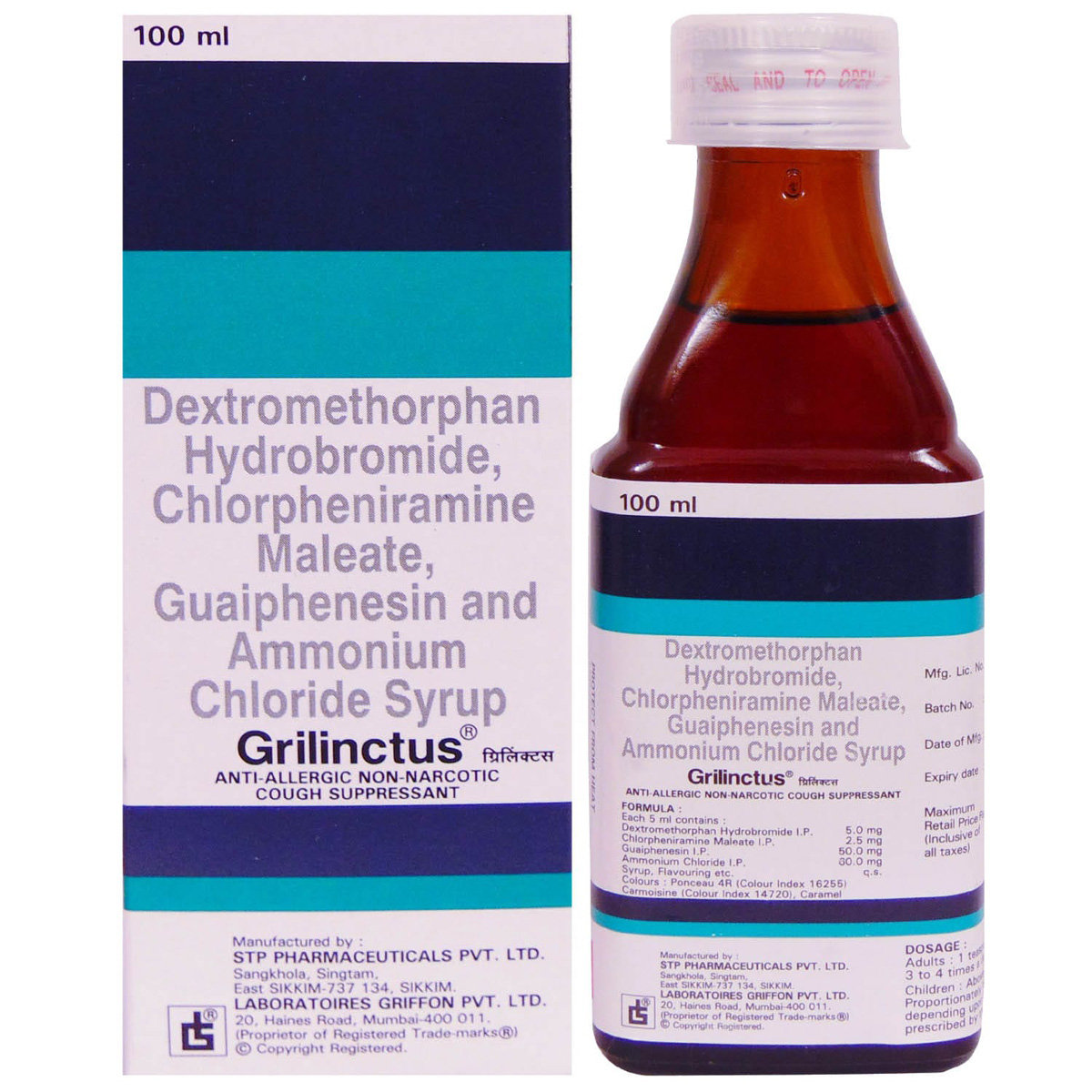
Grilinctus Syrup

MRP ₹133
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹19.9 Cashback (15%)
know your delivery time
Provide Delivery Location
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :
Selected Pack Size:100 ml
100 ml ₹117
(₹1.17 per ml)
Out of stock

Secure Payment

Trusted by 8 Crore Indians

Genuine Products
Therapeutic Class
Country of origin
Manufacturer/Marketer address
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
Disclaimer
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
Avoid consumption of alcohol with Grilinctus Syrup as it may increase adverse effects. Please consult a doctor before consuming alcohol with Grilinctus Syrup .
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
The safety of Grilinctus Syrup in pregnant women is unknown. Therefore, it is given to pregnant women only if the doctor thinks the benefits outweigh the risks.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
Please consult your doctor. Grilinctus Syrup is given to breastfeeding mothers only if the doctor thinks the benefits are greater than the risks.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
Grilinctus Syrup may impair thinking or cause blurred vision or dizziness in some people. Therefore, drive only if you are alert after taking Grilinctus Syrup .
Liver
Consult your doctor
Take Grilinctus Syrup with caution, especially if you have a history of Liver diseases/conditions. The dose may be adjusted by your doctor as required if you have severe liver disease.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
Take Grilinctus Syrup with caution, especially if you have a history of Kidney diseases/conditions. The dose may be adjusted by your doctor as required in severe kidney disease.
Children
Safe if prescribed
Grilinctus Syrup is not recommended for children below 12 years of age. Please consult a doctor if you have any concerns.
About Grilinctus Syrup
Grilinctus Syrup belongs to a class of medications called 'expectorants' primarily used to treat cough. Coughing (dry or productive) is the body's way of clearing irritants (like allergens, mucus or smoke) from airways and preventing infection. There are two types of coughs, namely: Dry cough and chesty cough. A dry cough is tickly and doesn't produce any vicious or thick mucus, while a chesty cough (wet cough) produces mucous or sputum.
Grilinctus Syrup contains Dextromethorphan, Chlorpheniramine, Guaiphenesin and Ammonium chloride. Dextromethorphan works by blocking the transmission of nerve signals from the cough centre in the brain to the muscles that produce cough, thereby decreasing the urge to cough. Chlorpheniramine blocks the action of histamine, which is responsible for causing allergic reactions. Guaiphenesin and Ammonium chloride increase the volume of fluid in the airways, reduce the stickiness of mucus and help to remove it from the airways. Together, Grilinctus Syrup helps provides relief from cough.
Your doctor will recommend the dose and duration of Grilinctus Syrup based on your medical condition. Some people may experience dry mouth, dry throat or nose, nausea, stomach upset, vomiting, drowsiness, headache, blurred vision, constipation, dizziness, restlessness or nervousness. Most of these side effects do not require medical attention and gradually resolve over time. However, if the side effects persist or worsen, please consult your doctor.
Consult your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Grilinctus Syrup is not recommended for children below 12 years of age. Grilinctus Syrup may cause drowsiness, so drive or operate machinery only if you are alert. Avoid alcohol consumption as it may lead to increased drowsiness. Keep your doctor informed about your health condition and medications to rule out any interactions.
Uses of Grilinctus Syrup
Medicinal Benefits Mweb
Key Benefits
Grilinctus Syrup is a combination of four drugs, namely: Dextromethorphan, Chlorpheniramine, Guaiphenesin and Ammonium chloride. Dextromethorphan belongs to the class of cough suppressants; it helps decrease the urge to cough. Chlorpheniramine is an antihistamine (antiallergic drug) that provides relief from symptoms of allergy such as sneezing, stuffy/runny nose, watery eyes, itching, swelling, and congestion or stiffness. Guaifenesin and Ammonium chloride belongs to the class of irritants and expectorants that work by increasing the volume of fluid in the airways, reducing the stickiness of mucus and helps to remove it from the airways. Together, Grilinctus Syrup provides relief from cough.
Directions for Use
Side Effects of Grilinctus Syrup
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Stomach upset
- Constipation
- Drowsiness
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness
- Restlessness or nervousness
Drug Warnings
Do not take Grilinctus Syrup if you are allergic to any of its components. Inform your doctor if you have high blood pressure, fits, glaucoma, hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), chronic bronchitis or emphysema (a lung condition causing shortness of breath), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), blockage in the stomach or intestines, phenylketonuria (a congenital disability that causes accumulation of amino acid, phenylalanine in the body), enlarged prostate, pheochromocytoma (tumour in the adrenal glands), kidney, liver, lung, heart or urinary problems.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Taking Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** and Potassium citrate (in tablet or capsule form) together can increase the risk of stomach ulcers, bleeding, and gastrointestinal injury.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** with Potassium citrate is not recommended as it can lead to an interaction, it can be taken if prescribed by the doctor. However, if you experience any symptoms such as severe stomach pain, bloating, lightheadedness or dizziness, nausea, vomiting (especially with blood), decreased hunger, or dark, tarry stools, consult the doctor immediately. Do not discontinue any medications without a doctor's advice.
Taking Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** and Potassium chloride (in tablet or capsule form) together can increase the risk of stomach ulcers, bleeding, and gastrointestinal injury.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** with Potassium chloride it not recommended as it can lead to an interaction, it can be taken if your doctor has prescribed it. However, if you experience any symptoms such as severe stomach pain, bloating, lightheadedness or dizziness, nausea, vomiting (especially with blood), decreased hunger, or dark, tarry stools, consult the doctor. Do not discontinue any medications without a doctor's advice.
Co-administration of Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** and Selegiline may increase the risk of serotonin syndrome (a condition in which a chemical called serotonin builds up in your body).
How to manage the interaction:
Co-administration of Selegiline with Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** can possibly result in an interaction, but it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. If you notice any of these symptoms - confusion, hallucination, fits, increased heart rate, fever, excessive sweating, shivering, shaking, blurred vision, muscle spasm, stiffness, incoordination, stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea - make sure to contact a doctor right away. Do not stop using any medications without talking to a doctor.
Taking Tranylcypromine with Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome (a condition in which a chemical called serotonin increases in your body).
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** with Tranylcypromine is not recommended, but can be taken together if prescribed by a doctor. However, consult a doctor if you experience confusion, hallucination(seeing and hearing things that do not exist), fit blood pressure alteration, increased heart rate, fever, excessive sweating, shivering or shaking, blurred vision, pain in the muscles or stiffness, incoordination, stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Co-administration of Phenelzine and Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome (A condition in which a chemical called serotonin builds up in your body).
How to manage the interaction:
Co-administration of Phenelzine and Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** can lead to an interaction. However, if you experience any symptoms like confusion, hallucination, seizure, changes in blood pressure, increased heart rate, fever, excessive sweating, shivering or shaking, blurred vision, muscle stiffness, tremors, stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, consult a doctor immediately. Do not stop using any medications without a doctor's advice.
Co-administration of Isocarboxazid with Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome (A condition in which a chemical called serotonin builds up in your body).
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** and Isocarboxazid can lead to an interaction. However, if you experience any symptoms like confusion, hallucination, seizure, changes in blood pressure, increased heart rate, fever, excessive sweating, shivering or shaking, blurred vision, muscle stiffness, tremors, stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, consult a doctor immediately. Do not stop using any medications without a doctor's advice.
Co-administration of Pargyline and Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome (A condition in which a chemical called serotonin builds up in your body).
How to manage the interaction:
Co-administration of Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** and Pargyline can lead to an interaction. However, if you experience any symptoms like confusion, hallucination, seizure, changes in blood pressure, increased heart rate, fever, excessive sweating, shivering or shaking, blurred vision, muscle stiffness, tremors, stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, consult a doctor immediately. Do not stop using any medications without a doctor's advice.
Co-administration of Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** and Procarbazine may increase the risk of serotonin syndrome (a condition in which a chemical called serotonin builds up in your body).
How to manage the interaction:
Co-administration of Procarbazine with Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** can possibly result in an interaction, but it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. If you notice any of these symptoms - confusion, hallucination, seizure, increased heart rate, fever, excessive sweating, shivering, shaking, blurred vision, muscle spasm, stiffness, incoordination, stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea - make sure to contact a doctor right away. Do not stop using any medications without talking to a doctor.
Taking Rasagiline with Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome (A condition in which a chemical called serotonin increase in your body).
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** with Rasagiline is not recommended as it can possibly result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. If you notice any of these symptoms like confusion, hallucination, fits, extreme changes in blood pressure, increased heart rate, fever, excessive sweating, shivering or shaking, blurred vision, muscle spasm or stiffness, shaking, incoordination, stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, consult a doctor. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Co-administration of Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** with Isocarboxazid can increase the risk of side effects.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Grilinctus Syrup 100ml *** with Isocarboxazid can result in an interaction, but it can be taken if your doctor has advised it. However, if you have any of these symptoms - dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, disorientation, memory problems, blurred vision, dry mouth, constipation, heat intolerance, flushing, decreased sweating, difficulty urinating, rapid heartbeat, - make sure to consult the doctor right away. Do not stop using any medications without talking to a doctor.
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List
- DIPHENHYDRAMINE
- CETIRIZINE
- DULOXETINE
- SERTRALINE
- ESCITALOPRAM
- METHADONE
- HYDROCODONE
- CODEINE
- HALOPERIDOL
- QUETIAPINE
- ALPRAZOLAM
- QUINIDINE
- AMIODARONE
- PREGABALIN
- AMPHETAMINE
Habit Forming
Special Advise
- You are recommended to inform the doctor that you are taking Grilinctus Syrup if you are undergoing any medical tests or surgery.
- It is advised to stop using Grilinctus Syrup if your cough persists for more than 1 week and it reoccurs or is accompanied by hay fever, skin rash or persistent fever.
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Avoid dairy products such as milk, as it may increase mucus production.
- Avoid processed or refined foods. Replace baked foods, fried foods, white bread, white pasta, French fries, sugary desserts and chips with green leafy vegetables.
- Drink plenty of fluids to avoid a dry throat. It also helps loosen mucus.
- Avoid citrus fruits as they may worsen the cough.
- Eat fruits rich in water content, such as pears, watermelon, peaches and pineapples.
Buy best Respiratory System products by
Cipla Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Abbott India Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
German Remedies Ltd
Centaur Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Pristine Pearl Pharma Pvt Ltd
Wockhardt Ltd
GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd
Koye Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Blue Cross Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Medishri Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Med Manor Organics Pvt Ltd
Indiabulls Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Adonis Laboratories Pvt Ltd
FDC Ltd
Fourrts India Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Tablets India Ltd
J B Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Shreya Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Divine Savior Pvt Ltd
Indoco Remedies Ltd
Seagull Pharmaceutical Pvt Ltd
Yash Pharma Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Torque Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Uniza Healthcare Llp
Wings Pharmacuticals Pvt Ltd
Biological E Ltd
Corona Remedies Pvt Ltd
Icarus Health Care Pvt Ltd
Steris Healthcare
Apex Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Geno Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Navil Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Precept Pharma
Aar Ess Remedies Pvt Ltd
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Astra Zeneca Pharma India Ltd
Biochem Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Comed Chemicals Ltd
Entod Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Franco Indian Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Healthgate Pvt Ltd
Intra Life Pvt Ltd
Megma Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Pfizer Ltd
RPG Life Sciences Ltd
Unipark Biotech Pvt Ltd
Votary Laboratories (India) Ltd
Wanbury Ltd
Brinton Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Dolvis Bio Pharma Pvt Ltd
Eisen Pharmaceutical Co Pvt Ltd
Group Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Knoll Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Panacea Biotec Ltd
Prevego Healthcare & Research Pvt Ltd
Rnd Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Sanatra Healthcare Ltd
Skn Organics Pvt Ltd
Stedman Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Thuyam Life Pvt Ltd
Timon Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Aglowmed Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Bio Warriors Pharmaceucticals Pvt Ltd
Biochemix Health Care Pvt Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Caplet India Pvt Ltd
Chemo Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Delcure Life Sciences Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Embiotic Laboratories (P) Ltd
Emcee Pharmaceuticals (P) Ltd
Foregen Healthcare Ltd
Hetero Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Incite Pharmaceuticals
Iva Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Kepler Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Kristal Pharmaceuticals
Lincoln Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Frequently Bought Together

_0.jpg?tr=q-85)




