Fourderm Cream
MRP ₹172.5
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹25.9 Cashback (15%)
know your delivery time
Provide Delivery Location
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :
Selected Pack Size:20 gm
20 gm ₹155.3
(₹7.77 per gm)
In Stock
10 gm ₹99.5
(₹9.95 per gm)
In Stock

Secure Payment

Trusted by 8 Crore Indians

Genuine Products
Therapeutic Class
Country of origin
Manufacturer/Marketer address
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
Disclaimer
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
Interaction of Fourderm Cream with alcohol is unknown. Please consult a doctor before consuming alcohol while using Fourderm Cream.
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
The safety of Fourderm Cream in pregnant women is unknown. Therefore, it is given to pregnant women only if the doctor thinks benefits outweigh risks.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
It is unknown whether Fourderm Cream is excreted in human milk. Please consult a doctor before using Fourderm Cream while breastfeeding.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
Fourderm Cream usually does not affect your ability to drive or operate machinery.
Liver
Consult your doctor
If you have any concerns regarding the use of Fourderm Cream in patients with Liver problems, please consult a doctor.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
If you have any concerns regarding the use of Fourderm Cream in patients with Kidney problems, please consult a doctor.
Children
Safe if prescribed
The safety of Fourderm Cream in children is unknown. Please consult a doctor.
Product Substitutes
Reference
- https://www.drugs.com/clobetasol-topical.html
- https://www.drugs.com/mtm/miconazole-topical.html
- https://www.drugs.com/cons/neomycin-topical.html#:~:text=Neomycin%20belongs%20to%20the%20family,are%20available%20without%20a%20prescription.
- https://www.drugs.com/drug-interactions/neomycin.html
- https://www.drugs.com/mtm/chlorhexidine-topical.html
About Fourderm Cream
Fourderm Cream belongs to a class of dermatological medication ‘Topical Anti-Infectives with Corticosteroids’ used to reduce swelling, itching, and redness caused due to certain skin infections caused by bacteria and fungus. Fungal infection is a skin disease in which a fungus attacks the tissue and causes infection. Fungal infections may be contagious (spread from one person to another). Bacterial infection is a condition in which harmful bacteria grow in the body and cause infection. It can infect any part of the body and multiply very quickly.
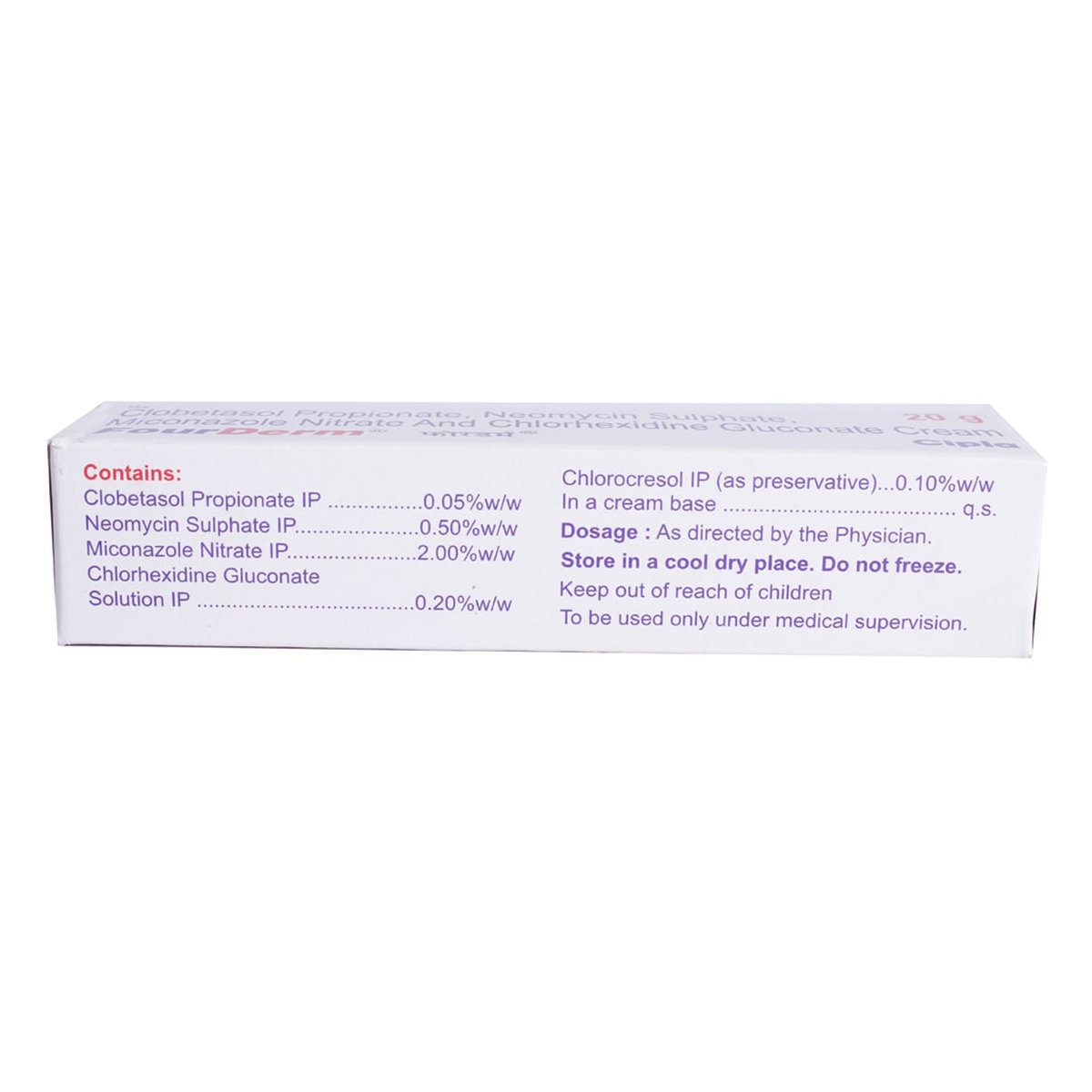
Fourderm Cream is a combination of four drugs, namely: Chlorhexidine (antiseptic), Clobetasol (corticosteroid), Miconazole (antifungal), and Neomycin (antibiotic). Chlorhexidine belongs to the class of antiseptics that works by killing the micro-organisms and thus, prevents infection. Clobetasol belongs to the class of corticosteroids that works by acting inside skin cells and inhibits the release of certain chemical messengers in the body that cause redness, itching, and swelling. Miconazole belongs to the class of antifungals that works by causing holes in the fungal cell membranes and kills fungi. Neomycin belongs to the class of antibiotics that works by inhibiting the production of essential proteins that are necessary for bacteria to grow, multiply and increase in numbers. Thereby, kills the bacteria and fungi preventing skin infection.
Fourderm Cream is only for external use. Use Fourderm Cream as prescribed. Avoid contact of Fourderm Cream with nose, ears, mouth, or eyes. In case Fourderm Cream comes in contact with these areas accidentally, rinse with water thoroughly. Some people may experience dry skin, skin rash, thinning of the skin, itching, swelling, redness, or burning sensation at the site of application. Most of these side effects of Fourderm Cream do not require medical attention and gradually resolve over time. However, if the side effects persist or worsen, please consult your doctor.
If you are known to be allergic to Fourderm Cream or any other medicines, please tell your doctor. If you are pregnant or a nursing mother, it is advised to consult a doctor before using Fourderm Cream. Fourderm Cream should be used with caution in infants below 2 months old if prescribed by a doctor as it may cause chemical burns or severe irritation on babies. Do not use Fourderm Cream in more than prescribed doses, or for a prolonged time as it may cause adverse effects. Avoid using Fourderm Cream on open skin wounds, deep cuts, or scrapes. Do not wrap or cover the treated area with bandages unless advised by your doctor. Do not swallow Fourderm Cream. In case of accidental swallowing, contact a nearby poison control center or consult a doctor immediately. If you have adrenal gland or liver problems and any skin infection, inform your doctor before taking Fourderm Cream.
Uses of Fourderm Cream
Medicinal Benefits Mweb
Key Benefits
Fourderm Cream is a combination of four drugs, namely: Chlorhexidine, Clobetasol, Miconazole, and Neomycin. Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic that kills microorganisms and prevents infection. Clobetasol is a corticosteroid that works by acting inside skin cells and inhibits the release of certain chemical messengers in the body that cause redness, itching, and swelling. Miconazole is an antifungal that works by causing holes in the fungal cell membranes and kills fungi. Neomycin is an antibiotic that works by inhibiting the production of essential proteins that are necessary for bacteria to grow, multiply and increase in numbers. Thereby, kills the bacteria and fungi preventing the spread of the skin infection.
Directions for Use
Side Effects of Fourderm Cream
- Dry skin
- Skin rash
- Thinning of the skin
- Itching, swelling, redness or burning sensation at the site of application
Drug Warnings
If you are known to be allergic to Fourderm Cream or any other medicines, please tell your doctor. If you are pregnant or a nursing mother, it is advised to consult a doctor before using Fourderm Cream. Fourderm Cream should be used with caution in infants below 2 months old if prescribed by a doctor as it may cause chemical burns or severe irritation on babies. Do not use Fourderm Cream in more than prescribed doses, or for a prolonged time as it may cause adverse effects. Avoid using Fourderm Cream on open skin wounds, deep cuts, or scrapes. Do not wrap or cover the treated area with bandages unless advised by your doctor. Do not swallow Fourderm Cream. In case of accidental swallowing, contact a nearby poison control center or consult a doctor immediately. If you have adrenal gland or liver problems and any skin infection, inform your doctor before taking Fourderm Cream.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List
- WARFARIN
- DICUMAROL
- ANISINDIONE
- METFORMIN
- BACITRACIN
- POLYMYXIN B
- FUROSEMIDE
Habit Forming
Special Advise
Please consult a dermatologist if your skin infection persists for more than 1 month.
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Regularly change your socks and wash your feet. Avoid shoes that make your feet sweaty and hot.
- In wet places such as changing rooms and gym showers, don’t walk on barefoot. Wear flip-flops or sandals to prevent fungal infections.
- Do not scratch the affected area of skin as it can spread the infection to other body parts.
- Avoid sharing towels, combs, bedsheets, shoes or socks with others to prevent the spread of infection.
- Wash your bed sheets and towels regularly.
- Eat foods rich in quercetin (a flavonoid) such as apples, cherry, broccoli, spinach and blueberries.
- Consuming food rich in probiotics helps in developing the immune system against allergies.
- Limit intake of food that might trigger allergies such as dairy products, soy, eggs, and nuts.
- Avoid consumption of foods with excess sugar as it may flare-up inflammation.
- Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats and fish in your diet.
- Avoiding getting in contact with harsh soaps, detergents and rough fabrics.
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
Out of StockMegmazole GM Cream 20 gm
Megma Healthcare Pvt Ltd
₹72
(₹3.24/ 1gm)
58% CHEAPERRX
Out of StockDermasol-GM Cream 15 gm
Shinto Organics Pvt Ltd
₹69.9
(₹4.19/ 1gm)
46% CHEAPER

Have a query?
Buy best Dermatology products by
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Klm Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Cipla Ltd
Canixa Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
Atopic laboratories Pvt Ltd
Hegde & Hegde Pharmaceutica Llp
Brinton Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Amwill Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Palsons Derma Pvt Ltd
Oaknet Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Med Manor Organics Pvt Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Dermocare Laboratories Gujarat Llp
Fixderma India Pvt Ltd
Apex Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Yaher Pharma
Systopic Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Menarini India Pvt Ltd
Ethinext Pharma
Nemus Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Skinocean Pharmaceuticals
Dermacia Healthcare
Inex Medicaments Pvt Ltd
Lupin Ltd
GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Talent India Pvt Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Kivi Labs Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Hbc Dermiza Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Mrhm Pharma Pvt Ltd
Regaliz Medicare Ltd
Sol Derma Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Newtrimed Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Wallace Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Eskon Pharma
Glowderma Lab Pvt Ltd
La Pristine Bioceuticals Pvt Ltd
Mohrish Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Percos India Pvt Ltd
Rockmed Pharma Pvt Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Praise Pharma
Ethicare Remedies Pvt Ltd
Kaizen Drugs Pvt Ltd
Aurel Biolife
Rely On Pharmaceuticals
Wockhardt Ltd
Galcare Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Indiabulls Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
La Med Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Biocute Life Care
Yap Bioceuticals
Yash Pharma Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Zee Laboratories Ltd
Apple Therapeutics Pvt Ltd
Adonis Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Albatross Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Galderma India Pvt Ltd
Prism Life Sciences Ltd
FDC Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Salve Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
West Coast Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Dermarex HealthCare India Pvt Ltd
Arka Vital Science Pvt Ltd
Dermajoint India
Gary Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Grace Derma Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Karlin Pharmaceuticals & Exports Pvt Ltd
Skinska Pharmaceutica Pvt Ltd
Uniza Healthcare Llp
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Cosmofix Technovation Pvt Ltd
Human Pharmaceuticals
Indolands Pharma Pvt Ltd
Lyra Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Entod Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Iceberg Health Care Pvt Ltd
Jenburkt Pharmaceuticals Ltd
P and P Dermaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Dabur India Ltd
Indchemie Health Specialities Pvt Ltd
Olcare Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Unison Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
BODY CREAM
Body Lotion
Face Cream
Shampoo
Sun Screen
Face Gel
Soap
Face Wash
HAIR SOLUTION
Face Serum
BODY GEL
Hair Lotion
Hair Serum
Dusting Powder
ANTISEPTIC
FACE CLEANSER
Face Lotion
Body Wash
Body Spray
Eye Cream
FUNGAL INFECTION
Foot Cream
Conditioner
Eye Gel
Cleanser
Hair Cream
Hair Oil
Face Mask
Hair Gel
Sanitizer
Hair Spray
Moisturiser
Skin Ointment
Lip Balm
Capsule
Eye Serum
Intimate Wash
Specialty Supplements
Hand Cream
Facial Spray
SPECIALITY SUPPLEMENT
Face Toner
MEDICATED SHAMPOO
Tablet
Talcum Powder
BABY SUNSCREEN
Body Butter
Body Scrub
DIAPER RASH CREAM
EYE SOLUTION
FACIAL WIPE
Gargle
Hand Wash
Intimate Spray
Lip Serum
Lubricant Gel
MEDICATED CREAM
Nail Polish
VITAMIN D
Customers Also Bought