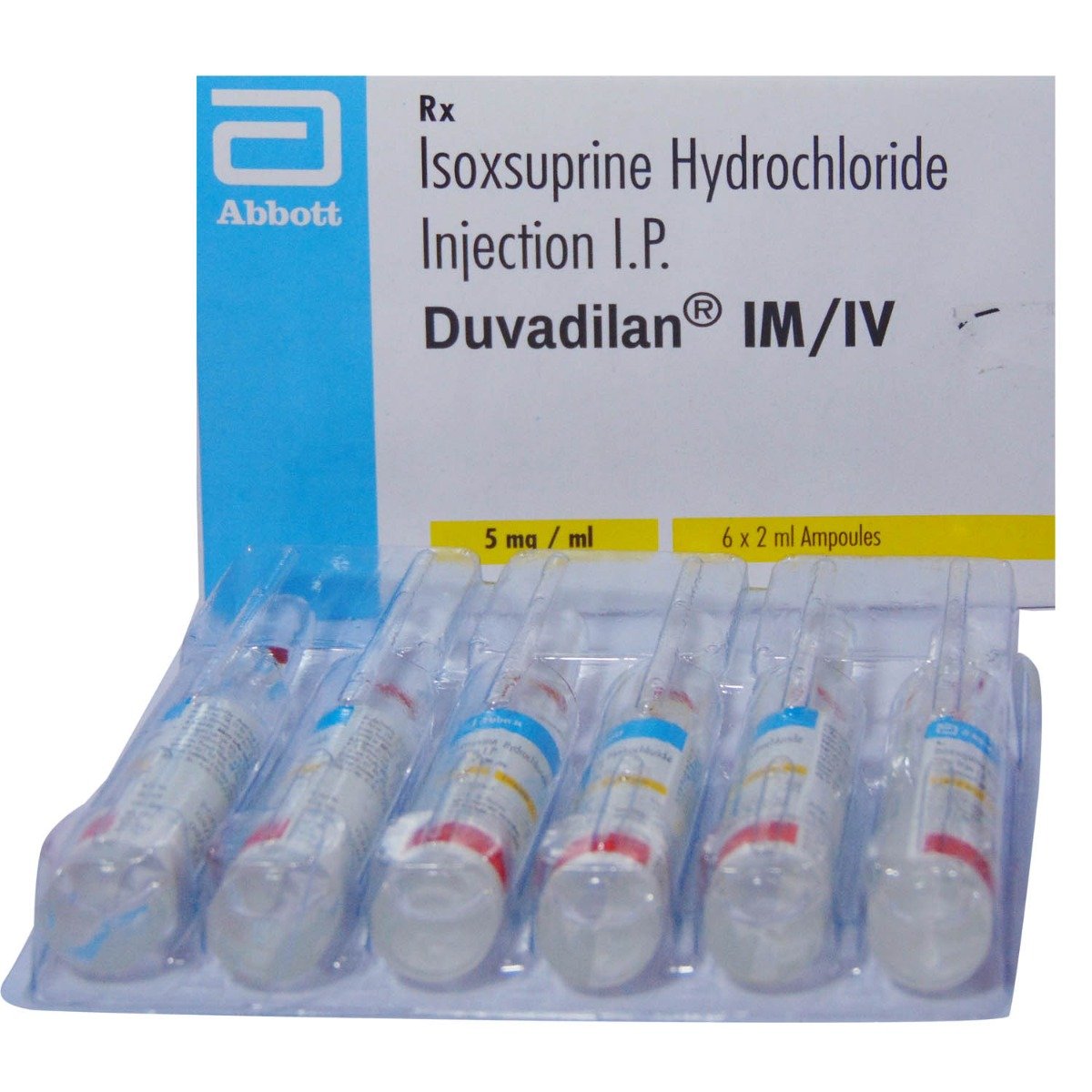
Duvadilan Injection 2 ml


MRP ₹33.5
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹5.0 Cashback (15%)
know your delivery time
Provide Delivery Location
Composition :
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :

Secure Payment

Trusted by 8 Crore Indians

Genuine Products
Therapeutic Class
Country of origin
Manufacturer/Marketer address
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
Disclaimer
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
Avoid alcohol consumption while on treatment with Duvadilan Injection 2 ml as it might cause increased dizziness.
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
Duvadilan Injection 2 ml should not be used when pregnancy unless clearly necessary. So, inform your doctor if you are pregnant. Your doctor will weigh the benefits and potential risks before prescribing Duvadilan Injection 2 ml.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
Duvadilan Injection 2 ml is not recommended to be used in breastfeeding unless clearly necessary. So, inform your doctor if you are a nursing mother. Your doctor will weigh the benefits and potential risks before prescribing Duvadilan Injection 2 ml.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
Drive with caution; Duvadilan Injection 2 ml may cause dizziness.
Liver
Consult your doctor
Inform your doctor before receiving the Duvadilan Injection 2 ml if you have a history of liver problems. Your doctor may adjust the dose of this medicine based on your liver condition.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
Inform your doctor before receiving the Duvadilan Injection 2 ml if you have a history of kidney conditions. Your doctor may adjust the dose of this medicine based on your kidney condition.
Children
Safe if prescribed
Duvadilan Injection 2 ml is not recommended for children as the safety and effectiveness of Duvadilan Injection 2 ml have not been established.
Product Substitutes
Keep Refrigerated. Do not freeze.
Reference
- https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682831.html
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/isoxsuprine-oral-route-injection-route/description/drg-20067777
- https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=908691b4-7950-4f3e-bbea-ea568fee7ac3
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/isoxsuprine-oral-route-injection-route/side-effects/drg-20067777?p=1#:~:text=Isoxsuprine%20belongs%20to%20the%20group,as%20determined%20by%20your%20doctor.
- https://www.mims.com/philippines/drug/info/duvadilan?type=full
- https://www.drugs.com/drug-interactions/isoxsuprine.html
About Duvadilan Injection 2 ml
Duvadilan Injection 2 ml belongs to a class of medication called 'vasodilators' (blood vessel relaxing agents). It is used to treat and prevent peripheral vascular diseases such as Raynaud's phenomenon, cerebral vascular insufficiency (poor blood flow to the brain), arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), Buerger's disease (a condition that causes small and medium arteries and veins to constrict blood flow to the hands and feet) and other conditions involving poor blood flow in the blood vessels. It is also used for relaxing uterine muscles to prevent premature labour.
Duvadilan Injection 2 ml contains Isoxsuprine hydrochloride. It works by relaxing and widening the blood vessels, thereby improving blood circulation. Thus, it helps treat peripheral vascular diseases. Duvadilan Injection 2 ml relaxes and prevents the contractions of smooth muscles of the uterus and prevents premature labour.
Duvadilan Injection 2 ml is administered by a healthcare professional; do not self-administer. Sometimes, Duvadilan Injection 2 ml may cause dizziness, irregular heartbeat, nausea, vomiting, and weakness as side effects. Most of these side effects do not require medical attention and gradually resolve over time. However, if these side effects persist, inform your doctor.
Duvadilan Injection 2 ml may not be safe for all. Inform your doctor before taking Duvadilan Injection 2 ml if you have any bleeding disorder or heart problems. Duvadilan Injection 2 ml may cause a sudden fall in blood pressure, so be cautious if you are driving, operating a motor vehicle or doing any hazardous task. Do not stand suddenly from a lying or sitting position, as you may feel dizzy after taking this medicine. Avoid consuming alcohol with Duvadilan Injection 2 ml as it may cause dizziness.
Uses of Duvadilan Injection 2 ml
Medicinal Benefits Mweb
Key Benefits
Duvadilan Injection 2 ml contains Isoxsuprine hydrochloride, which is a vasodilator. It is used in the treatment of cerebrovascular insufficiency (poor blood flow to the brain), peripheral vascular disease (blocked veins of the leg), Buerger's disease (a condition that causes small and medium arteries and veins to constrict blood flow to the hands and feet), arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and Raynaud's disease (numb and cold sensation due to blocked nerves of hand). Duvadilan Injection 2 ml acts by relaxing and widening the blood vessels, thereby improving blood circulation. Thus, it helps to treat peripheral vascular diseases. Duvadilan Injection 2 ml relaxes and prevents the contractions of smooth muscles of the uterus, and prevents premature labour.
Directions for Use
Side Effects of Duvadilan Injection 2 ml
- Weakness
- Dizziness
- Flushing
- Irregular heartbeat
- Stomach upset
- Vomiting
Drug Warnings
Inform your doctor if you are allergic to any of the components, have low blood pressure (less than 90 mm of Hg), have had a heart problem, or bleeding problem. Tell your doctor that you are using Duvadilan Injection 2 ml before undergoing any dental or other surgery. Your doctor might stop this medicine before the surgery. Duvadilan Injection 2 ml should not be stopped abruptly without consulting the doctor as it may lead to unpleasant side effects. Also, lifestyle changes should be continued with Duvadilan Injection 2 ml for best results and a speedy recovery. Duvadilan Injection 2 ml may cause dizziness, so if you are sitting, rise slowly to avoid falling and be cautious while driving or operating machinery.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Co-administration of Duvadilan Injection 2 ml and tizanidine may lead to low blood pressure, which may result in side effects.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Tizanidine with Duvadilan Injection 2 ml together can possibly result in an interaction, but it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. However, if you experience headache, lightheadedness, fainting, changes in pulse or heart rate, consult a doctor. Do not stop using any medications without talking to a doctor.
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Habit Forming
Special Advise
- Use caution while driving a motor vehicle, operating machinery, or performing other hazardous activities as Duvadilan Injection 2 ml may cause dizziness. If you experience dizziness or drowsiness, avoid these activities. Try to rise slowly from a sitting or lying position to avoid falling.
- Notify your doctor if you experience skin rash or palpitations (irregular heartbeats) after using Duvadilan Injection 2 ml.
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Opt for a diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products.
- Quitting smoking is the best strategy to lower the risk of heart disease.
- Avoid stress. Try to enjoy and spend time with your loved ones to cope with stress and practice mindfulness techniques.
- Reduce intake of fatty food, sugar and salt.
- Limit or avoid alcohol consumption.
- Strenuous exercise or work should be avoided to avoid delivery complications.
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
TIDILAN INJECTION 2ML
Juggat Pharma Ltd
₹28
(₹12.6/ 1ml)
16% CHEAPER

Have a query?
Buy best Cardiology products by
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Cipla Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Eris Life Sciences Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Lloyd Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
USV Pvt Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Elbrit Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
J B Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Alteus Biogenics Pvt Ltd
Hbc Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Fusion Health Care Pvt Ltd
Troikaa Pharmaceuticals Ltd
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Corona Remedies Pvt Ltd
Jubilant Lifesciences Ltd
Medley Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Knoll Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Msn Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Blue Cross Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Lividus Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Ranmarc Labs
Shrrishti Health Care Products Pvt Ltd
Sanofi India Ltd
Steris Healthcare
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Primus Remedies Pvt Ltd
Unison Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Eswar Therapeutics Pvt Ltd
Knoll Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Tas Med India Pvt Ltd
Systopic Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Indiabulls Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Sinsan Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Biochem Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Azkka Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Nirvana India Pvt Ltd
Orsim Pharma
Prevego Healthcare & Research Pvt Ltd
Econ Healthcare
Elinor Pharmaceuticals (P) Ltd
FDC Ltd
Sunij Pharma Pvt Ltd
Nicholas Piramal India Ltd
Astra Zeneca Pharma India Ltd
Pfizer Ltd
Lia Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Shine Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Elicad Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Indoco Remedies Ltd
Proqol Health Care Pvt Ltd
Vasu Organics Pvt Ltd
Biocon Ltd
Opsis Care Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Johnlee Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Merck Ltd
Wockhardt Ltd
Auspharma Pvt Ltd
Ergos Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Lakshya Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Ordain Health Care Global Pvt Ltd
Pficus De Med Pvt Ltd
ALICAN PHARMACEUTICAL PVT LTD
RPG Life Sciences Ltd
Glynis Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Orris Pharmaceuticals
Samarth Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Aprica Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Aretaeus Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Koye Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Neocardiab Care
Retra Life Science Pvt Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Alvio Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Arkas Pharma Pvt Ltd
Atos Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Divine Savior Pvt Ltd
Metalis Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Frequently Bought Together
Customers Also Bought


_0.jpg?tr=q-85)