Duovir Tablet


MRP ₹215.5
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹32.3 Cashback (15%)
know your delivery time
Provide Delivery Location
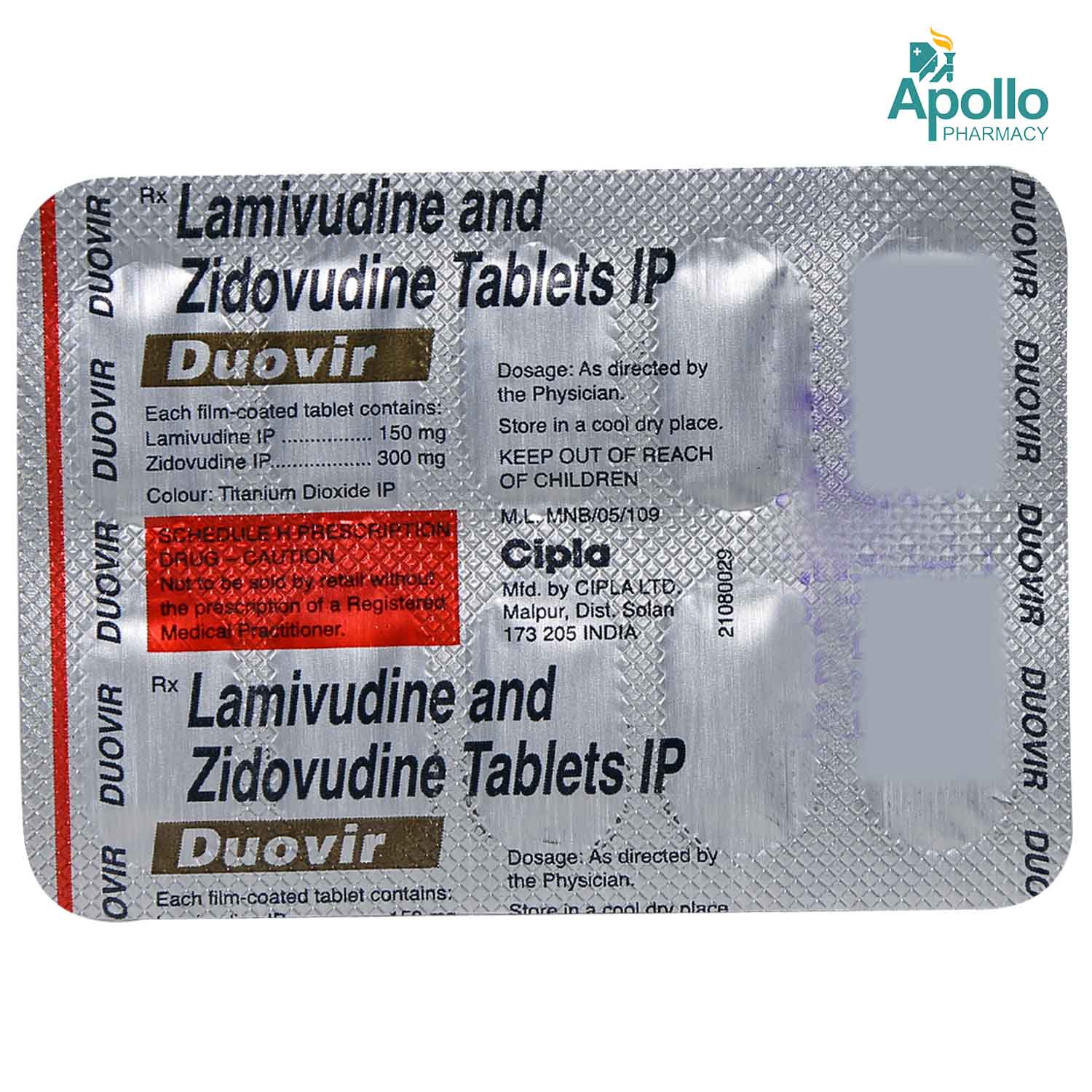
Composition :
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :
NPPA :
Selected Pack Size:10
10 ₹193.95
(₹19.4 per unit)
Out of stock
60 ₹1195.7
(₹19.93 per unit)
In Stock

Secure Payment

Trusted by 8 Crore Indians

Genuine Products
Therapeutic Class
Country of origin
Manufacturer/Marketer address
FAQs
Disclaimer
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
Duovir Tablet with alcohol can cause unpleasant side effects. So please consult your doctor before consumption of alcohol while taking Duovir Tablet .
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
Duovir Tablet is not recommended for use in pregnant women unless necessary. All the risks and benefits should be discussed with the doctor before taking this medicine.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
Duovir Tablet is not recommended for use in breastfeeding women unless necessary. All the risks and benefits should be discussed with the doctor before taking this medicine. Your doctor may advise you to discontinue the drug or breastfeeding based on your clinical condition.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
Duovir Tablet may cause dizziness or sleepiness. Don't drive or do anything requiring concentration until you know how it affects you.
Liver
Consult your doctor
Duovir Tablet should be used with caution in liver patients due to the increased risk of worsening the patient's condition. So please consult your doctor before taking Duovir Tablet .
Kidney
Consult your doctor
Duovir Tablet should be used with caution in kidney patients due to the increased risk of serious side effects. So please consult your doctor before taking Duovir Tablet .
Children
Safe if prescribed
Duovir Tablet should be used with caution in Children. Your doctor may prescribe Duovir Tablet by adjusting the dose based on the height and weight of the children.
Product Substitutes
Reference
- https://www.mims.com/malaysia/drug/info/lamivudine%20+%20zidovudine?mtype=generic
- https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/2998/smpc#PRODUCTINFO
- https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-4666/lamivudine-zidovudine-oral/details
- https://www.drugs.com/mtm/lamivudine-and-zidovudine.html
- https://www.drugs.com/mtm/lamivudine-and-zidovudine.html
About Duovir Tablet
Duovir Tablet belongs to the class of medicines called 'anti-retroviral agents', used for the treatment of immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system. If HIV is not treated, it can lead to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). This medicine is not a cure for HIV. It only prevents the virus from multiplying in your body.
Duovir Tablet contains lamivudine and zidovudine. Duovir Tablet works by preventing HIV (virus) from multiplying, thereby reducing the amount of virus in your body. They also increase the CD4 cell (white blood cells that protect against infection) count in your blood.
Take Duovir Tablet as advised by your doctor. Duovir Tablet may cause common side effects like nausea, diarrhoea, headache, fatigue, cough, a feeling of discomfort, and nasal congestion (stuffy nose). Most of these side effects gradually resolve over time and do not require medical attention. However, if these side effects persist or worsen, please consult your doctor immediately.
Inform your doctor if you are allergic to any of the components in Duovir Tablet . Please consult your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to conceive or breastfeeding. Let your doctor know if you have kidney, liver, or pancreatic disease. Please tell your doctor if you have a low red blood cell count (anaemia), low white blood cell count (neutropenia), osteonecrosis (death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood supply), or lactic acidosis.
Uses of Duovir Tablet
Medicinal Benefits Mweb
Key Benefits
Duovir Tablet contains a combination of two medicines, namely: lamivudine and zidovudine, that belong to the group of medications called anti-retroviral agents. Duovir Tablet is primarily used for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Duovir Tablet works by preventing HIV (virus) from multiplying, thereby reducing the amount of virus in your body. They also increase the CD4 cell (white blood cells that protect against infection) count in your blood.
Directions for Use
Side Effects of Duovir Tablet
- Nausea
- Diarrhoea
- Stomach pain
- Loss of appetite
- Tiredness
- Lack of energy
- Fever (high temperature)
- Headache
- Hair loss (alopecia)
- Fatigue
- Cough
- Muscle pain and discomfort
- Joint pain
- Feeling of discomfort
- Difficulty in sleeping (insomnia)
- Irritated or runny nose
Drug Warnings
Inform your doctor if you are allergic to any of the components in Duovir Tablet . Please consult your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to conceive or breastfeeding. Let your doctor know if you have kidney, liver, pancreatic, or bone marrow suppression. Please tell your doctor if you have a low red blood cell count (anaemia), low white blood cell count (neutropenia), osteonecrosis (death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood supply), lactic acidosis, or opportunistic infections. Duovir Tablet may cause muscle disorders, especially when used for a long period. Tell your doctor if you have or have ever had any disease of the muscles or muscle weakness. If you experience muscle pain or muscle weakness, call your doctor immediately.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Combining these two medications may reduce overall effectiveness due to potential antagonistic effects (opposite actions).
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Emtricitabine with Duovir Tablet is not recommended, but it can be taken if your doctor prescribes it. Contact your doctor if your symptoms do not improve. Do not stop taking any medication without consulting your doctor.
Teriflunomide can cause Duovir Tablet to stay in the body longer, leading to higher levels in the blood.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction between Duovir Tablet and Teriflunomide, you can take these medicines together if prescribed by your doctor. If you have any of these signs and symptoms, contact your doctor immediately: fever, chills, pain, swelling, bruising, skin rash, itching, loss of appetite, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark-coloured urine, or bleeding. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting your doctor.
Taking Duovir Tablet and mipomersen together can increase the risk of liver damage.
How to manage the interaction:
Although taking Duovir Tablet and Mipomersen together can evidently cause an interaction, it can be taken if your doctor has suggested it. If you have any of these symptoms, it's important to contact your doctor right away. These symptoms include fever, rash, itching, loss of appetite, feeling sick, feeling tired, pain in the upper right side of your belly, dark urine, yellowing of the skin or eyes, chills, joint pain, swelling, bruising, loss of appetite, and bleeding. Do not stop using any medications without talking to your doctor.
Combining Duovir Tablet with Leflunomide can increase the risk and severity of muscle problems.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction between Duovir Tablet and Leflunomide, you can take these medicines together if prescribed by your doctor. If you have any of these symptoms it's important to contact your doctor right away: fever, feeling cold, joint discomfort, swelling, bruising, skin irritation, itching, not feeling hungry, tiredness, feeling sick, stomach ache, dark urine or bleeding. Do not stop using any medications without talking to your doctor.
Taking Duovir Tablet and lomitapide together can increase the risk of liver damage
How to manage the interaction:
There may be a possibility of interaction between Duovir Tablet and Lomitapide, but it can be taken if prescribed by a doctor. If you have any of these symptoms, it's important to contact your doctor right away. These symptoms include fever, rash, itching, loss of appetite, feeling sick, feeling tired, feeling unwell, pain in the upper right side of your stomach, dark urine, yellowing of the skin or eyes, chills, joint pain, swelling, bruising, stomach pain, liver damage, or bleeding. Do not stop using any medications without a doctor's advice.
Combining these two medications may reduce overall effectiveness due to potential antagonistic effects (opposite actions).
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction between Duovir Tablet and Zalcitabine, you can take these medicines together if prescribed by your doctor. Contact your doctor if your symptoms do not improve. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting your doctor.
Taking bexarotene together with Duovir Tablet increases the risk of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
How to manage the interaction:
There may be a possibility of interaction between Duovir Tablet and Bexarotene, but it can be taken if prescribed by a doctor. If you're having symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain, contact your doctor right away. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting your doctor.
Duovir Tablet can cause higher levels of Sorbitol in the blood by reducing its excretion rate.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Sorbitol with Duovir Tablet together can possibly result in an interaction, but it can be taken if your doctor has advised it. Do not stop using any medications without talking to your doctor.
When Etanercept is used with Duovir Tablet, the likelihood or severity of infection may increase.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Etanercept with Duovir Tablet together can result in an interaction, but it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. However, if you develop fever, chills, diarrhea, sore throat, muscular pains, shortness of breath, blood in phlegm, weight loss, red or irritated skin, body sores, or discomfort or burning during urination, consult a doctor immediately. Do not discontinue any medications without a doctor's advice.
Taking Duovir Tablet with Tofacitinib may increase the risk of serious infection.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction between Tofacitinib and Duovir Tablet, you can take these medicines together if prescribed by your doctor. However, consult the doctor immediately if you experience symptoms such as fever, chills, diarrhea, sore throat, muscle aches, shortness of breath, blood in phlegm, weight loss, red or inflamed skin, body sores, and pain or burning during urination. Do not stop using any medications without first talking to your doctor.
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Frozen Meals, Cheese, Red Meat, Potato Chips, Hamburgers, Hot Dogs, Ice Cream
How to manage the interaction:
Consuming high-fat foods along with Duovir Tablet may decrease its effectiveness. Avoid or limit the consumption of high-fat foods with Duovir Tablet as it can increase the risk of side effects.
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List
- DIDANOSINE
- EFAVIRENZ
- ATOVAQUONE
- CLARITHROMYCIN
- GANCICLOVIR
- COTRIMOXAZOLE
- FLUCONAZOLE
- RIFAMPICIN
- PHENOBARBITAL
- PHENYTOIN
- VALPROIC ACID
- RANITIDINE
- CIMETIDINE
- CLADRIBINE
- PROBENECID
- METHOTREXATE
- ATORVASTATIN
- FENOFIBRATE
- CLOZAPINE
Habit Forming
Special Advise
- Skipping doses of Duovir Tablet may increase the risk of treatment failure. Make sure that you take all your doses at the correct time.
- Always practice safe sex while taking Duovir Tablet . Do not share needles or personal items that can have blood or body fluids on them.
- Exercise regularly and take calcium and vitamin D supplements as suggested by your doctor because Duovir Tablet may cause the weakening of your bones.
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Take a diet high in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes.
- Choose lean, low-fat sources of protein.
- Limit sweets, soft drinks, and foods with added sugar.
- Take proteins, carbohydrates, and a good little fat in all meals and snacks in your regular diet.
- Avoid eating raw eggs, meats, or seafood (including sushi and oysters/shellfish).
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly.
- Use a separate cutting board for raw meats.
- Wash hands, utensils, and cutting boards with soap and water after each use.
- Exercise regularly.
- Avoid excessive alcohol and quit smoking.
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
Out of StockVIROCOMB FC 150MG TABLET
Crossland
₹1236.6
(₹18.55 per unit)
4% CHEAPERRX
Out of StockZovilam 150mg/300mg Tablet
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
₹1245
(₹18.68 per unit)
3% CHEAPERRX
Out of StockZIDOVEX L TABLET
Aurobindo Pharma Ltd
₹63.9
(₹19.17 per unit)
1% CHEAPER

Have a query?
Buy best Infections & Infestation products by
Cipla Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
FDC Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Biochem Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd
United Biotech Pvt Ltd
Hetero Drugs Ltd
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Indoco Remedies Ltd
Fusion Health Care Pvt Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Wockhardt Ltd
Zydus Cadila
GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Blue Cross Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Converge Biotech Pvt Ltd
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Hetero Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Pfizer Ltd
AAA Pharma Trade Pvt Ltd
Gufic Bioscience Ltd
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Corona Remedies Pvt Ltd
Wallace Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Apex Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Medishri Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Hegde & Hegde Pharmaceutica Llp
Veritaz Healthcare Ltd
Ranbaxy Laboratories Ltd
Koye Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Shreya Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Overseas Health Care Pvt Ltd
Biocon Ltd
Indchemie Health Specialities Pvt Ltd
Medley Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Brinton Pharmaceuticals Ltd
J B Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Unifaith Biotech Pvt Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Biochemix Health Care Pvt Ltd
Natco Pharma Ltd
Samarth Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Unichem International
Laborate Pharmaceuticals India Ltd
Unipark Biotech Pvt Ltd
Zymes Bioscience Pvt Ltd
Indiabulls Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Neon Laboratories Ltd
Vasu Organics Pvt Ltd
DR Johns Lab Pharma Pvt Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Medgen Drugs And Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Novartis India Ltd
Canixa Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Icarus Health Care Pvt Ltd
Lincoln Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Celon Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Concept Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Klm Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Nicholas Piramal India Ltd
Systopic Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Yuventis Pharmaceuticals
Capital Pharma
German Remedies Ltd
Pristine Pearl Pharma Pvt Ltd
Unison Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Aurz Pharmaceutical Pvt Ltd
Clover Health Care Pharma
Kepler Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Allites Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Auspharma Pvt Ltd
Intra Life Pvt Ltd
Jolly Healthcare
Linux Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Ozone Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Cachet Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Comed Chemicals Ltd
Delcure Life Sciences Ltd
Fresenius Kabi India Pvt Ltd
Khandelwal Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Frequently Bought Together








