Atenex 50 Tablet

MRP ₹27.5
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹4.1 Cashback (15%)
know your delivery time
Provide Delivery Location
Composition :
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :

Secure Payment

Trusted by 8 Crore Indians

Genuine Products
Therapeutic Class
Country of origin
Manufacturer/Marketer address
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
Disclaimer
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
Avoid alcohol consumption while taking Atenex 50 Tablet as it may cause dizziness or lightheadedness.
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
Atenex 50 Tablet should not be taken until prescribed. Atenex 50 Tablet is a Category D pregnancy drug. Pregnant mothers should exercise caution during pregnancy before taking Atenex 50 Tablet as it has been shown to cross the placental barrier and linked with intrauterine growth restriction.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
Caution should be exercised, and it is advisable to consult a doctor before using it. Your doctor will weigh the benefits and any potential risks before prescribing them to you. Risk of neonatal hypoglycemia (low blood sugar level) and bradycardia (slow heartbeat or rate).
Driving
Safe if prescribed
Drive only if you are physically stable and mentally focussed. You may experience dizziness after taking this medication; you should not drive or operate any machinery or vehicles.
Liver
Consult your doctor
Atenex 50 Tablet to be taken with caution, especially if you have a history of Liver diseases/conditions. The dose may have to be adjusted by your doctor. Please consult your doctor.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
Atenex 50 Tablet is not recommended for kidney failure patients or those at a severe kidney damage level. Please consult your doctor. Your doctor will weigh the benefits and any potential risks before prescribing them to you.
Children
Safe if prescribed
Atenex 50 Tablet is not recommended for children below 12 years of age. Please consult your doctor for more information.
Product Substitutes
Reference
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539844/
- https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/files/pil.6024.pdf
- https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/atenolol/
- https://www.drugs.com/drug-interactions/atenolol-index.html?filter=3
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539844/#:~:text=Mechanism%20of%20Action,-Cardioselective%20beta%2D1&text=%5B2%5D%20This%20activity%20results%20in,resulting%20in%20increased%20oxygen%20demand.
About Atenex 50 Tablet
Atenex 50 Tablet belongs to a group of heart disease-related medicines known as beta-blockers. It helps in the treatment of high blood pressure (hypertension), irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), and chest pain with painful tightness in the chest (angina pectoris). It protects the heart in the early treatment after a heart attack (myocardial infarction). High blood pressure increases the heart's workload, and if it continues for a long time, the heart and blood vessels (arteries) may not function properly. It can damage the arteries of the brain, heart, and kidneys, resulting in a stroke, heart failure, or kidney failure. However, lowering blood pressure may reduce the risk of stroke and heart attacks.
Atenex 50 Tablet contains atenolol, which primarily helps relax our blood vessels by blocking the action of certain natural substances in your body. Thus, Atenex 50 Tablet helps lower your raised blood pressure and reduce the risk of having a stroke, a heart attack, other heart problems, or kidney problems in the future.
Your doctor will advise you on how often you take Atenex 50 Tablet based on your medical condition. Sometimes, you may experience headaches, cold hands/feet, diarrhoea, feeling sick (nausea), tired, aching muscles, depressed mood, and dizziness. Most of these side effects of Atenex 50 Tablet do not require medical attention and gradually resolve over time. However, if the side effects persist, contact your doctor.
Don't stop taking Atenex 50 Tablet without talking to your doctor first. Stopping Atenex 50 Tablet gradually may cause heart rhythm and blood pressure changes and cause chest pain or a heart attack. Your doctor will lower your dose slowly over some time to help prevent these symptoms. If you are a pregnant woman or nursing mother, do not consume Atenex 50 Tablet without consulting your doctor. Talk to your doctor before taking the Atenex 50 Tablet if you have a very slow heartbeat, asthma, diabetes, thyrotoxicosis (thyroid gland disorders), serious heart condition (sick sinus syndrome) or any heart blockage, and severe kidney disease. Atenex 50 Tablet is not recommended for children below 12 years. Before taking the Atenex 50 Tablet , inform your doctor about your medical history and ongoing therapies to rule out potential adverse effects or interactions.
Uses of Atenex 50 Tablet
Medicinal Benefits Mweb
Key Benefits
Atenex 50 Tablet contains atenolol, which primarily helps relax our blood vessels by blocking the action of certain natural substances in your body. Thus, Atenex 50 Tablet helps lower your raised blood pressure and reduce the risk of having a stroke, a heart attack, other heart problems, or kidney problems in the future. This medicine needs to be taken regularly to be effective.
Directions for Use
Side Effects of Atenex 50 Tablet
- Headache
- Cold hands/feet
- Diarrhoea
- Feeling sick (nausea)
- Feeling tired
- Aching and tired muscles
- Depressed mood
- Dizziness
Drug Warnings
Atenex 50 Tablet should not be used in patients who have a cardiogenic shock (the heart is unable to pump enough blood), congestive heart failure, bradycardia (a very slow heartbeat), anuria (the kidneys are unable to make urine), or are allergic to this product. Don't stop taking Atenex 50 Tablet without first consulting your doctor. Stopping Atenex 50 Tablet suddenly may result in changes in heart rhythm and blood pressure, as well as chest pain or a heart attack. To help prevent these side effects, your doctor will gradually reduce your dose over time. Atenex 50 Tablet is not recommended in children below 12 years. The use of Atenex 50 Tablet could mask diabetes symptoms. So, if you have diabetes, inform your doctor. If you take Atenex 50 Tablet with anticoagulants like warfarin, you should check your prothrombin time on a regular basis.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Taking verapamil with Atenex 50 Tablet can increase the risk or severity of verapamil side effects.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Atenex 50 Tablet and Verapamil together can result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. However, if you experience, fatigue, headache, fainting, swelling of the extremities, weight gain, shortness of breath, chest pain, increased or decreased heartbeat, or irregular heartbeat, contact a doctor immediately. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Using dolasetron together with Atenex 50 Tablet can increase the risk of an irregular heart rhythm that may be serious.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there is a possible interaction between Atenex 50 Tablet and Dolasetron, you can take these medicines together if prescribed by a doctor. If you have any of these symptoms, like feeling dizzy, lightheaded, or your heart beating irregularly, it's important to call a doctor right away. Do not stop using any medications without talking to a doctor.
Coadministration of Atenex 50 Tablet with aminophylline could certainly reduce the efficacy of Atenex 50 Tablet and enhance the effects of aminophylline.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Atenex 50 Tablet alongside aminophylline can result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. However, if you experience nausea, vomiting, insomnia, tremors, restlessness, uneven heartbeats, or difficulty breathing, contact a doctor immediately. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Using Atenex 50 Tablet with theophylline, could increase the effects of theophylline.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Atenex 50 Tablet and theophylline together can result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. However, if you experience nausea, vomiting, insomnia, shaking of hands and legs, restlessness, uneven heartbeats, or difficulty breathing, contact the doctor immediately. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Coadministration of Atenex 50 Tablet and Nebivolol may increase the risk of irregular heart rhythm.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Atenex 50 Tablet and Nebivolol together can result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
When Bisoprolol is combined with Atenex 50 Tablet the severity or risk of side effects may be increased.
How to manage the interaction:
Although there may be an interaction, Atenex 50 Tablet can be taken with bisoprolol if prescribed by the doctor. Consult the prescriber if you experience any unusual side effects. Do not discontinue the medication without consulting a doctor.
Coadministration of Atenex 50 Tablet with ceritinib can slow heart rate and increase the risk of an irregular heart rhythm.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Atenex 50 Tablet and ceritinib together can result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. However, if you experience dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting, or an irregular heartbeat while taking these medications, consult the doctor immediately. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Coadministration of Tizanidine and Atenex 50 Tablet can increase the risk or severity of side effects like low blood pressure.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Atenex 50 Tablet and tizanidine together may result in an interaction, it can be taken if your doctor has recommended it. However, if you experience headache, dizziness, lightheadedness, sweating, or palpitations, consult the doctor. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
The use of atazanavir with Atenex 50 Tablet may raise the risk of an abnormal heart rhythm.
How to manage the interaction:
The combination of Atenex 50 Tablet and acebutolol may result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has advised it. However, if you develop sudden dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting, or irregular heartbeat, contact the doctor immediately. Do not stop using any medications without a doctor's advice.
Taking Atenex 50 Tablet and diltiazem together may lead to increased side effects.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Atenex 50 Tablet and diltiazem together can result in an interaction, it can be taken if a doctor has recommended it. However, if you experience tiredness, headache, fainting, swelling of the extremities, weight gain, shortness of breath, chest discomfort, increased or reduced heartbeat, or irregular heartbeat, consult the doctor. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting doctor.
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Pepperoni, Miso Soup, Natto, Shoyu, Shrimp, Ricotta, Salami, Stilton Cheese, Swiss Cheese, Tamari, Tempeh, Fish, Farm Cheese, Fava Beans, Fermented Seafood, Fermented Tofu, Gorgonzola Cheese, Chicken Liver, Chocolates, Cottage Cheese, Cream Cheese, Dried Sausage, Dry-Type Summer Sausages, Cheddar Cheese, Cashews, Camembert, Beef Liver, American Cheese, Almonds, Avocado, Wheat Germ, Bananas, Beef, Chicken, Eggs, Turkey, Soya Beans, Milk, Peanuts, Pork
How to manage the interaction:
Consumption of large amounts of orange juice while taking Atenex 50 Tablet may decrease the effievtiveness of Atenex 50 Tablet. Avoid consumption of large amounts of orange juice during treatment with Atenex 50 Tablet.
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Conventional hemodialysis removes Atenex 50 Tablet to a moderate extent. To prevent significant drops in blood pressure, patients on hemodialysis should get a dosage of Atenex 50 Tablet after each dialysis session while they are hemodynamically stable. Before and after the dose, the hemodynamic condition should be closely monitored.
How to manage the interaction:
Atenex 50 Tablet when taken before hemodialysis gets mildly eliminated, therefore to mitigate substantial declines in blood pressure you are advised to take a dose of Atenex 50 Tablet followed by your dialysis session in a hemodynamically stable condition.
The kidneys remove Atenex 50 Tablet. Patients with a creatinine clearance of 35 mL/min/1.73 m2 have significant medication accumulation. For some patients, dosage modifications are suggested.
How to manage the interaction:
Significant accumulation of the Atenex 50 Tablet occurs in patients with a creatinine clearance below 35 mL/min/1.73 m2. You are advised to consult your doctor for dose modifications
Patients with sinus bradyarrhythmia or heart block greater than the first degree should not use beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking medications. The use of beta-blockers is likely to make these situations worse because of their detrimental inotropic and chronotropic effects on the heart.
How to manage the interaction:
The use of Atenex 50 Tablet is likely to exacerbate conditions such as slow heart rate, heart block. Therefore you are advised to take it cautiously.
In general, individuals with overt congestive heart failure (CHF) should not be treated with beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking medications, also known as beta-blockers. Beta-blockade can aggravate heart failure because sympathetic activation may be crucial in maintaining hemodynamic function in these patients. However, in some CHF patients who are adequately compensated and using digitalis, diuretics, an ACE inhibitor, and/or nitrates, beta-blocker medication may be advantageous and can be taken judiciously.
How to manage the interaction:
If you have a serious cardiac issue such as very slow heartbeats, or heart failure, you should not take Atenex 50 Tablet.Do not discontinue Atenex 50 Tablet without first consulting your doctor. Stopping abruptly may aggravate your issue.
Beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking medications, also known as beta-blockers, can hide hypoglycemic symptoms such as tremors, tachycardia, and changes in blood pressure. Furthermore, nonselective beta-blockers might prevent catecholamine-mediated glycogenolysis, which would intensify insulin-induced hypoglycemia and prolong the return to normal blood glucose levels. Larger doses of beta-1-selective medicines may also exhibit these effects because cardioselectivity is not absolute. When treating individuals on beta-blockers who have diabetes or are prone to sudden hypoglycemia, caution should be exercised.
How to manage the interaction:
If Atenex 50 Tablet is necessary in diabetic individuals,it should be taken with care. Although it may hide rapid heart rate caused by low blood sugar levels, other symptoms such as dizziness and sweating may be unaffected.It does not aggravate insulin-induced low sugar levels at prescribed dosages and, does not prolong the blood sugar recovery to normal levels.
Higher reactivity to the offending allergens may be linked to the use of beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking medications in patients with a history of allergic reactions or anaphylaxis. During beta-blocker therapy, attacks may become more frequent and/or more severe.
How to manage the interaction:
If you are allergic to Atenex 50 Tablet, or if you are undergoing allergy treatments or skin tests, you should use it cautiously.
Using beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking medications (also known as beta-blockers) over an extended period of time may result in increased sensitivity to catecholamines. In individuals with coronary artery disease, exacerbations of angina, myocardial infarction, and ventricular arrhythmias have been seen in response to sudden medication discontinuation. When necessary, beta-blocker medication should be stopped gradually in patients with coronary insufficiency over the course of one to two weeks with progressive dosage reductions. Patients should be warned not to stop taking their medications without first speaking to their doctor. Beta-blocker therapy should typically be resumed, at least briefly, in patients who experience an aggravation of angina after discontinuing it, along with other clinically relevant therapies.
How to manage the interaction:
You should not abruptly discontinue using Atenex 50 Tablet. Stopping abruptly may aggravate your issue.If you are being treated for high blood pressure, continue to take this medication even if you feel OK. Symptoms of high blood pressure are not always present. You might require blood pressure medication for the rest of your life.
Beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking drugs, often known as beta-blockers, decrease cardiac output and may cause or exacerbate symptoms of arterial insufficiency in patients with peripheral vascular disease because of their detrimental inotropic and chronotropic effects on the heart. Additionally, by inhibiting beta-2 receptors in peripheral arteries, nonselective beta-blockers may reduce catecholamine-mediated vasodilation during exercise. Patients with peripheral vascular disease should receive beta-blocker therapy with caution. It is essential to keep a close eye on the arterial obstruction's development.
How to manage the interaction:
Do not discontinue Atenex 50 Tablet without first consulting your doctor. Stopping abruptly may aggravate your issue.
In general, beta-blockers, particularly cardioselective beta-blockers, should not be administered to patients with bronchospasm. Cardioselective beta-blockers may be used in individuals with bronchospastic illness who do not respond to or cannot tolerate other antihypertensive medications due to their relative beta-1 selectivity. It is best to use these drugs at the lowest dose possible because beta-1 selectivity is not always present. To prevent the increased plasma levels brought on by the longer dosing intervals, think about giving smaller doses. If the dosage must be raised, splitting the dose may be an option to reduce peak blood levels. It is advised to have bronchodilators, such as beta-2 agonists, on hand or to deliver them simultaneously if necessary.
How to manage the interaction:
Atenex 50 Tablet in general, Should not be used in patients with asthma.it should be used with caution in individuals with asthma who do not react to or cannot tolerate alternative medications for lowering blood pressure . If the dose needs be raised, dividing it should be explored to attain lower peak blood levels.
In general, beta-blockers, particularly cardioselective beta-blockers, should not be administered to patients with bronchospasm. Cardioselective beta-blockers may be used in individuals with bronchospastic illness who do not respond to or cannot tolerate other antihypertensive medications due to their relative beta-1 selectivity. It is best to use these drugs at the lowest dose possible because beta-1 selectivity is not always present. To prevent the increased plasma levels brought on by the longer dosing intervals, think about giving smaller doses. If the dosage must be raised, splitting the dose may be an option to reduce peak blood levels. It is advised to have bronchodilators, such as beta-2 agonists, on hand or to deliver them simultaneously if necessary.
How to manage the interaction:
Atenex 50 Tablet in general, Should not be used in patients with asthma.it should be used with caution in individuals with asthma who do not react to or cannot tolerate alternative medications for lowering blood pressure . If the dose needs be raised, dividing it should be explored to attain lower peak blood levels.
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List
- AMLODIPINE
- CLONIDINE
- ASPIRIN
- CHLORTHALIDONE
- HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE
- IBUPROFEN
- CLONAZEPAM
- FUROSEMIDE
- LEVOTHYROXINE SODIUM
- SILDENAFIL
- ALPRAZOLAM
- THEOPHYLLINE
- INDOMETHACIN
- INSULIN HUMAN
- QUINIDINE
- AMIODARONE
- DIGOXIN
- ADRENALINE
Habit Forming
Special Advise
- Patients with hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), lung disease (asthma) and diabetes should inform a doctor before taking Atenex 50 Tablet . The doctor may suggest an appropriate diagnostic test before prescribing Atenex 50 Tablet to you.
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Keep your weight under control with BMI (Body Mass Index) 19.5-24.9.
- Do regular physical activity or exercise for at least 150 minutes per week, or about 30 minutes most days of the week. Doing this can help you to lower your raised blood pressure by about 5 mm of Hg.
- Opt for a diet rich in whole grains, fruits, veggies, and low-fat dairy products.
- Limiting sodium chloride (table salt) in your daily diet to 2300 mg per day or less than 1500 mg is ideal for most adults.
- Quitting smoking is the best strategy to lower the risk of heart disease.
- Avoid chronic stress as it can raise your blood pressure. Try to enjoy and spend time with your loved ones to cope with stress and practice mindfulness techniques.
- Monitor your blood pressure daily and if there is too much fluctuation, then immediately contact your doctor.
- Include heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids containing food and drinks in your daily diet. You can also use low-fat cooking oil like olive oil, soybean oil, canola oil, and coconut oil to help lower your elevated blood pressure.
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
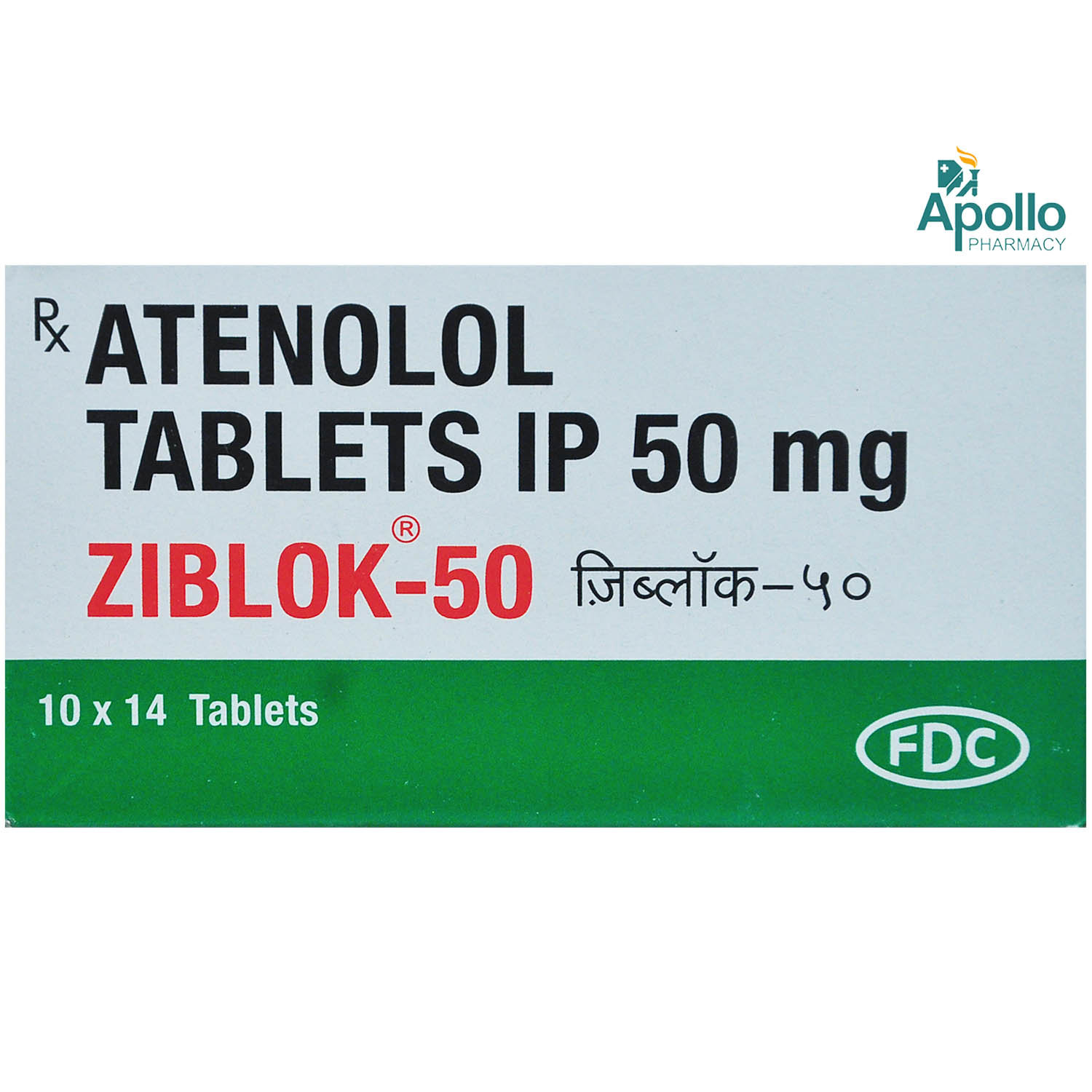
Ziblok-50 Tablet 14's
FDC Ltd
₹10.5
(₹0.68 per unit)
61% CHEAPERRX
UTL-50 Tablet 14's
Unison Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
₹14.5
(₹0.94 per unit)
46% CHEAPERRX
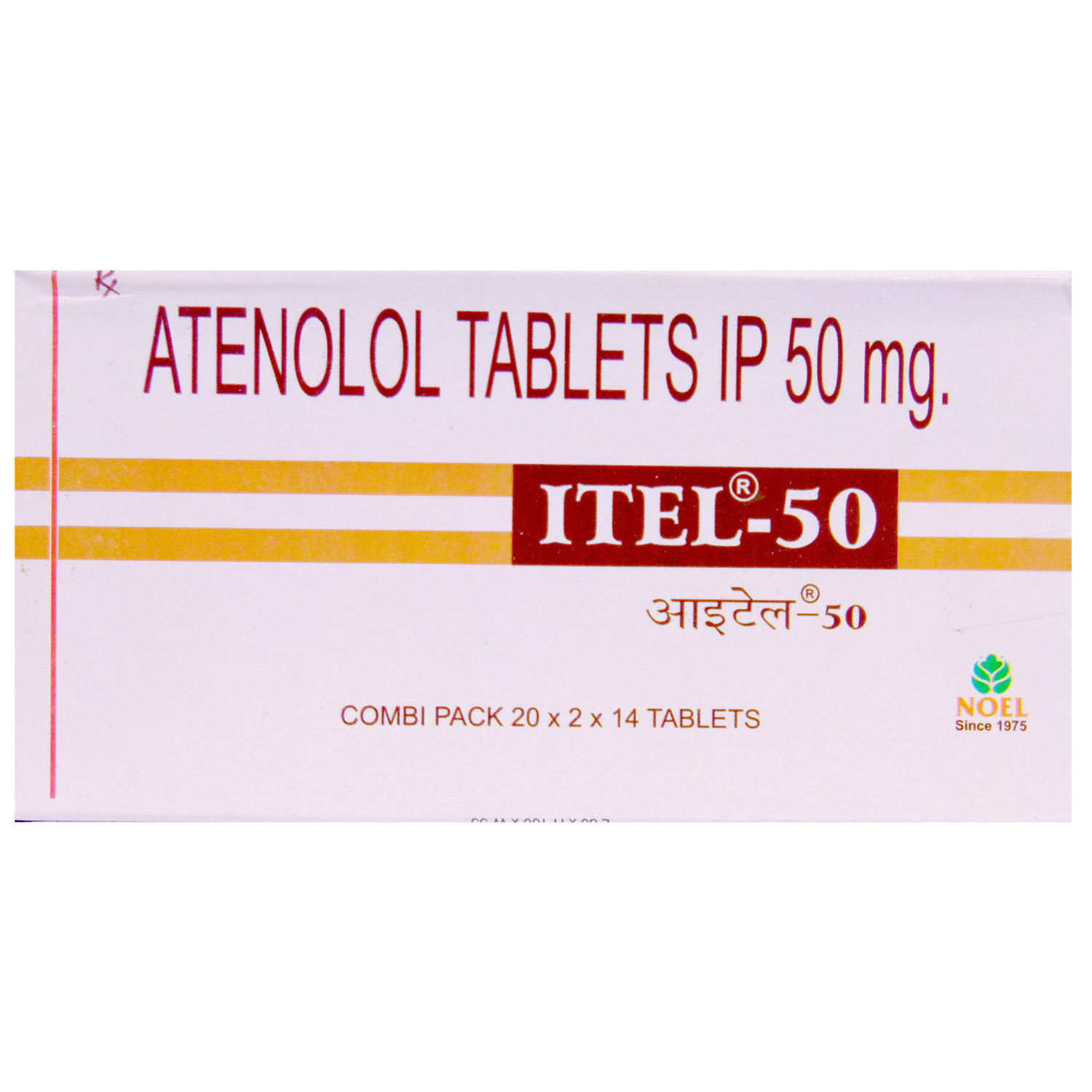
Itel-50 Tablet 14's
Noel Pharma India Pvt Ltd
₹22.5
(₹1.45 per unit)
18% CHEAPER

Have a query?
Buy best Cardiology products by
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Cipla Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Eris Life Sciences Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Lloyd Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
USV Pvt Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Elbrit Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
J B Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Alteus Biogenics Pvt Ltd
Hbc Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Fusion Health Care Pvt Ltd
Troikaa Pharmaceuticals Ltd
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Corona Remedies Pvt Ltd
Jubilant Lifesciences Ltd
Medley Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Knoll Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Msn Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Blue Cross Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Lividus Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Ranmarc Labs
Shrrishti Health Care Products Pvt Ltd
Sanofi India Ltd
Steris Healthcare
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Primus Remedies Pvt Ltd
Unison Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Eswar Therapeutics Pvt Ltd
Knoll Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Tas Med India Pvt Ltd
Systopic Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Indiabulls Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Sinsan Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Biochem Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Azkka Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Nirvana India Pvt Ltd
Orsim Pharma
Prevego Healthcare & Research Pvt Ltd
Econ Healthcare
Elinor Pharmaceuticals (P) Ltd
FDC Ltd
Sunij Pharma Pvt Ltd
Nicholas Piramal India Ltd
Astra Zeneca Pharma India Ltd
Pfizer Ltd
Lia Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Shine Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Elicad Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Indoco Remedies Ltd
Proqol Health Care Pvt Ltd
Vasu Organics Pvt Ltd
Biocon Ltd
Opsis Care Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Johnlee Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Merck Ltd
Wockhardt Ltd
Auspharma Pvt Ltd
Ergos Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Lakshya Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Ordain Health Care Global Pvt Ltd
Pficus De Med Pvt Ltd
ALICAN PHARMACEUTICAL PVT LTD
RPG Life Sciences Ltd
Glynis Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Orris Pharmaceuticals
Samarth Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Aprica Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Aretaeus Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Koye Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Neocardiab Care
Retra Life Science Pvt Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Alvio Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Arkas Pharma Pvt Ltd
Atos Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Divine Savior Pvt Ltd
Metalis Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Frequently Bought Together
₹155.7
MRP ₹173
10% off
1
+₹185.3
MRP ₹234
21% off
1
+₹223.9
MRP ₹271.5
18% off
1
+₹333
MRP ₹370
10% off
1
+₹168.8
MRP ₹187.5
10% off
1
+₹49.9
MRP ₹56
11% off
1
+₹175.5
MRP ₹195
10% off
1
+₹176
MRP ₹195.5
10% off
1
+₹279.5
MRP ₹310.5
10% off
1
+₹135.6
MRP ₹154.5
12% off
6
+Recommended for a 30-day course: 2 Strips