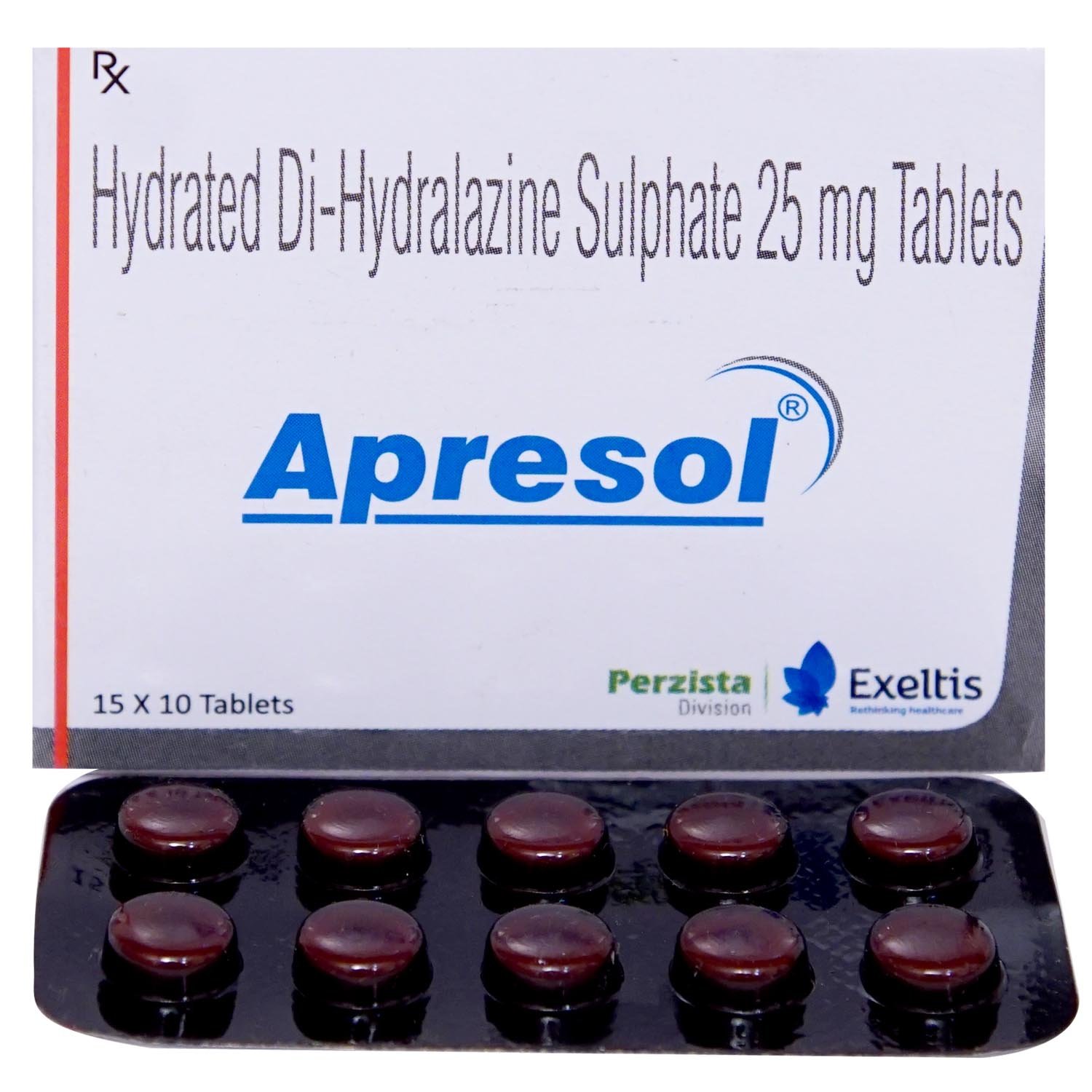
Apresol Tablet


MRP ₹81
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹12.2 Cashback (15%)
know your delivery time
Provide Delivery Location
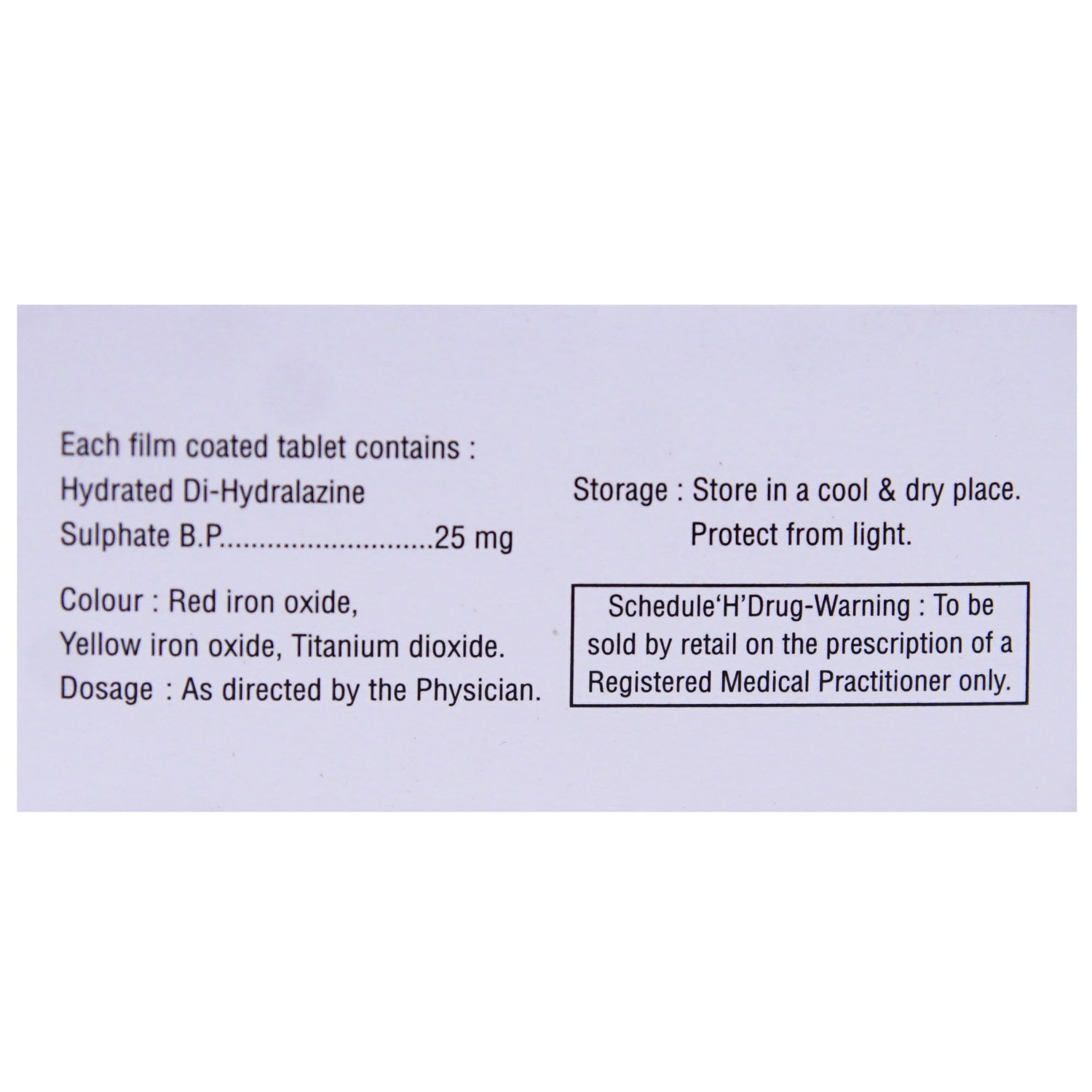
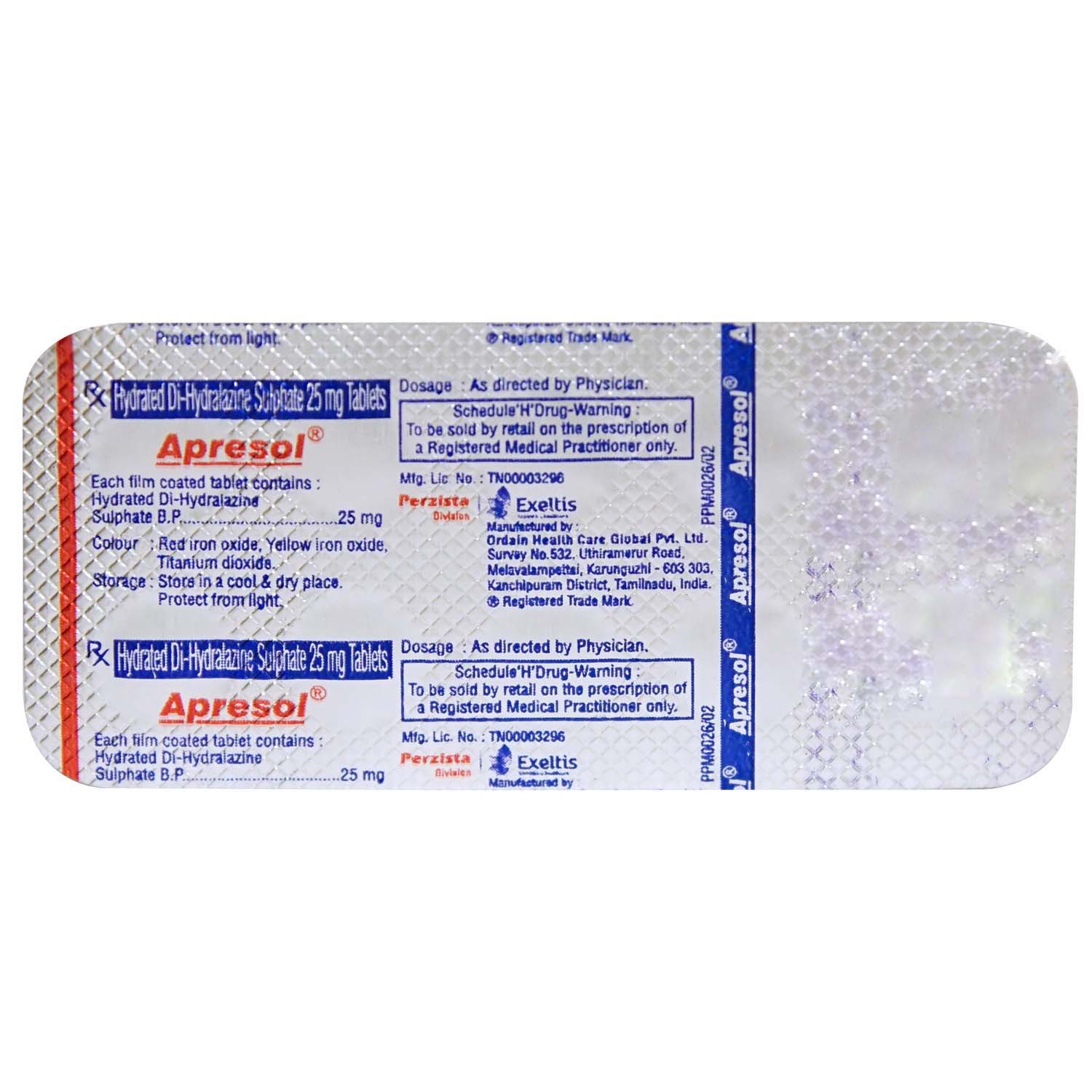
Composition :
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :
Selected Pack Size:10
10 ₹72.9
(₹7.29 per unit)
In Stock
15 ₹119.7
(₹7.98 per unit)
In Stock
30 ₹294.4
(₹9.81 per unit)
In Stock

Secure Payment

Trusted by 8 Crore Indians

Genuine Products
Therapeutic Class
Country of origin
Manufacturer/Marketer address
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
Disclaimer
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
You are recommended not to consume alcohol along with Apresol Tablet to avoid unpleasant side-effect of low blood pressure causing dizziness or drowsiness.
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
Apresol Tablet is a category C pregnancy drug. Apresol Tablet is not recommended during pregnancy unless your doctor considers it essential. Your doctor will weigh the benefits and any potential risks before prescribing it to you.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
Take Apresol Tablet only when prescribed, it is known to pass on in a limited quantity via breast milk to the child. Your doctor will weigh the benefits and any potential risks before prescribing it to you.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
Apresol Tablet is unlikely to affect your ability to drive or to operate machinery. However, some people may occasionally feel dizzy or tired when taking Propranolol. If this happens to you, ask your doctor for advice.
Liver
Consult your doctor
Apresol Tablet to be taken with caution, especially if you have a history of Liver diseases/conditions. The dose may have to be adjusted by your doctor.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
Apresol Tablet to be taken with caution, especially if you have a history of Kidney diseases/conditions. The dose may have to be adjusted by your doctor.
Children
Safe if prescribed
The safety and efficacy of Apresol Tablet in children have not been established. Apresol Tablet is not recommended in children.
Product Substitutes
About Apresol Tablet
Apresol Tablet belongs to a group of medicines called 'antihypertensive' used alone or together with other medicines to treat high blood pressure (hypertension), heart-related chest pain (angina), heart rhythm disorder (arrhythmia) and preventing symptoms of migraine headache and tremors (fits). It affects our heart and blood circulatory system, especially controlling blood pressure through arteries and veins. High blood pressure adds to the workload of the heart and arteries. If it continues for a long time, the heart and arteries may not function properly. This can damage the blood vessels of the brain, heart, and kidneys, resulting in a stroke, heart failure, or kidney failure. Lowering blood pressure may reduce the risk of stroke and heart attacks.
Apresol Tablet belongs to a class of drugs called ‘peripheral vasodilators’ which acts on the blood vessels directly and relaxes them, resulting in lowered blood pressure levels. Thus, it helps in reducing your risk of having a stroke, a heart attack, other heart problems, or kidney problems in the future. This medicine needs to be taken regularly to be effective.
Apresol Tablet can be taken orally with or without food or as directed by your physician. Swallow the whole tablet with a glass of water. Do not crush, chew, or break it. Apresol Tablet is preferable to take at the same time every day for better results. Apresol Tablet is generally safe to consume. You may have a common side like an abnormal heartbeat, headaches, low blood pressure, diarrhoea, and feeling sick and being sick. These side effects are usually mild and short-lived. However, if the side effects are persistent, reach out to your doctor.
Don't stop taking $ name without talking to your doctor first. Stopping Apresol Tablet gradually may cause changes in your heart rhythm and blood pressure, cause chest pain, or a heart attack. Your doctor will lower your dose gradually over a period of time to help prevent these symptoms. You should not use Apresol Tablet if you have a very slow heartbeat, asthma, serious heart condition (sick sinus syndrome), or any heart blockage. It should not be given to the children less than 12 years of age. Before taking Apresol Tablet , you should tell the doctor if you have any muscle disorder (myasthenia gravis, rhabdomyolysis), breathing problem (COPD, bronchitis, emphysema), low blood sugar level (hypoglycaemia), low blood pressure (hypotension), depression, previous heart failure, liver/kidney disease, thyroid hormone disorder, adrenal gland cancer, or problems with circulation (Raynaud’s syndrome).
Uses of Apresol Tablet
Medicinal Benefits Mweb
Key Benefits
Apresol Tablet plays a vital role in relaxing the muscles in the walls of your blood vessels. This ensures that your blood vessels expand, reducing your blood pressure and allowing blood and oxygen to flow more easily throughout your body and helps in reducing your risk of having a stroke, a heart attack, other heart problems, or kidney problems in the future. This medicine needs to be taken regularly to be effective.
Directions for Use
Side Effects of Apresol Tablet
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Fast heart rate
Drug Warnings
Don't stop taking $ name without talking to your doctor first. Stopping Apresol Tablet gradually may cause changes in your heart rhythm and blood pressure, cause chest pain, or a heart attack. Your doctor will lower your dose gradually over a period of time to help prevent these symptoms. You should not use Apresol Tablet if you have a very slow heartbeat, asthma, serious heart condition (sick sinus syndrome), or any heart blockage. Children weighing less than 4.5 pounds should not be given Apresol Tablet . It should not be given to the children less than 12 years of age. Before taking Apresol Tablet you should tell the doctor if you have any muscle disorder (myasthenia gravis, rhabdomyolysis), breathing problem (COPD, bronchitis, emphysema), low blood sugar level (hypoglycaemia), low blood pressure (hypotension), depression, previous heart failure, liver/kidney disease, thyroid hormone disorder, adrenal gland cancer, or problems with circulation (Raynaud’s syndrome).
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List
- DIAZOXIDE
- ISOCARBOXAZID
- TRANYLCYPROMINE
- PHENELZINE
- LINEZOLID
- METHYLENE BLUE
- RASAGILINE
- SELEGILINE
Habit Forming
Special Advise
Monitor your blood pressure daily and if there is too much of fluctuation then immediately contact your doctor.
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Keep your weight under control with BMI 19.5-24.9.
- Do regular physical activity or exercise for at least 150 minutes per week, or about 30 minutes most days of the week. Doing this can help you to lower your raised blood pressure by about 5 mm of Hg.
- Option for a diet rich in whole grains, fruits, veggies and low-fat dairy products.
- Limit intake of sodium chloride (table salt) in your daily diet to 2300 mg per day or less than 1500 mg is ideal for most adults.
- If you are taking alcohol then only one serving for women and two servings for men is advisable.
- Quitting smoking is the best strategy to lower the risk of heart disease.
- Avoid chronic stress as it can raise your blood pressure. Try to enjoy and spent time with your loved ones to cope with stress and practice mindfulness techniques.
- Try to include heart-healthy omega 3 fatty acid containing food drinks in your daily diet. You can also use low-fat cooking oil like olive oil, soybean oil, canola oil, and coconut oil can help in lowering your elevated blood pressure.
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
Out of StockHydral-25 Tablet 10's
Vajra Life Science Pvt Ltd
₹72
(₹6.48 per unit)
11% CHEAPERRX
Out of StockNepresol 25mg Tablet
Novartis India Ltd
₹80
(₹7.2 per unit)
1% CHEAPERRX
Apresol 25 Tablet 30's
Exeltis India
₹327
(₹9.81 per unit)
34% COSTLIER

Have a query?
Buy best Cardiology products by
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Cipla Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Eris Life Sciences Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Lloyd Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
USV Pvt Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Elbrit Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
J B Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Alteus Biogenics Pvt Ltd
Hbc Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Fusion Health Care Pvt Ltd
Troikaa Pharmaceuticals Ltd
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Corona Remedies Pvt Ltd
Jubilant Lifesciences Ltd
Medley Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Knoll Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Msn Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Blue Cross Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Lividus Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Ranmarc Labs
Shrrishti Health Care Products Pvt Ltd
Sanofi India Ltd
Steris Healthcare
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Primus Remedies Pvt Ltd
Unison Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Eswar Therapeutics Pvt Ltd
Knoll Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Tas Med India Pvt Ltd
Systopic Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Indiabulls Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Sinsan Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Biochem Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Azkka Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Nirvana India Pvt Ltd
Orsim Pharma
Prevego Healthcare & Research Pvt Ltd
Econ Healthcare
Elinor Pharmaceuticals (P) Ltd
FDC Ltd
Sunij Pharma Pvt Ltd
Nicholas Piramal India Ltd
Astra Zeneca Pharma India Ltd
Pfizer Ltd
Lia Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Shine Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Elicad Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Indoco Remedies Ltd
Proqol Health Care Pvt Ltd
Vasu Organics Pvt Ltd
Biocon Ltd
Opsis Care Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Johnlee Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Merck Ltd
Wockhardt Ltd
Auspharma Pvt Ltd
Ergos Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Lakshya Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Ordain Health Care Global Pvt Ltd
Pficus De Med Pvt Ltd
ALICAN PHARMACEUTICAL PVT LTD
RPG Life Sciences Ltd
Glynis Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Orris Pharmaceuticals
Samarth Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Aprica Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Aretaeus Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Koye Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Neocardiab Care
Retra Life Science Pvt Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Alvio Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Arkas Pharma Pvt Ltd
Atos Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Divine Savior Pvt Ltd
Metalis Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Frequently Bought Together
Customers Also Bought
Recommended for a 30-day course: 3 Strips