Addphos Granules

MRP ₹22.5
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹2.7 Cashback (12%)
know your delivery time
Provide Delivery Location
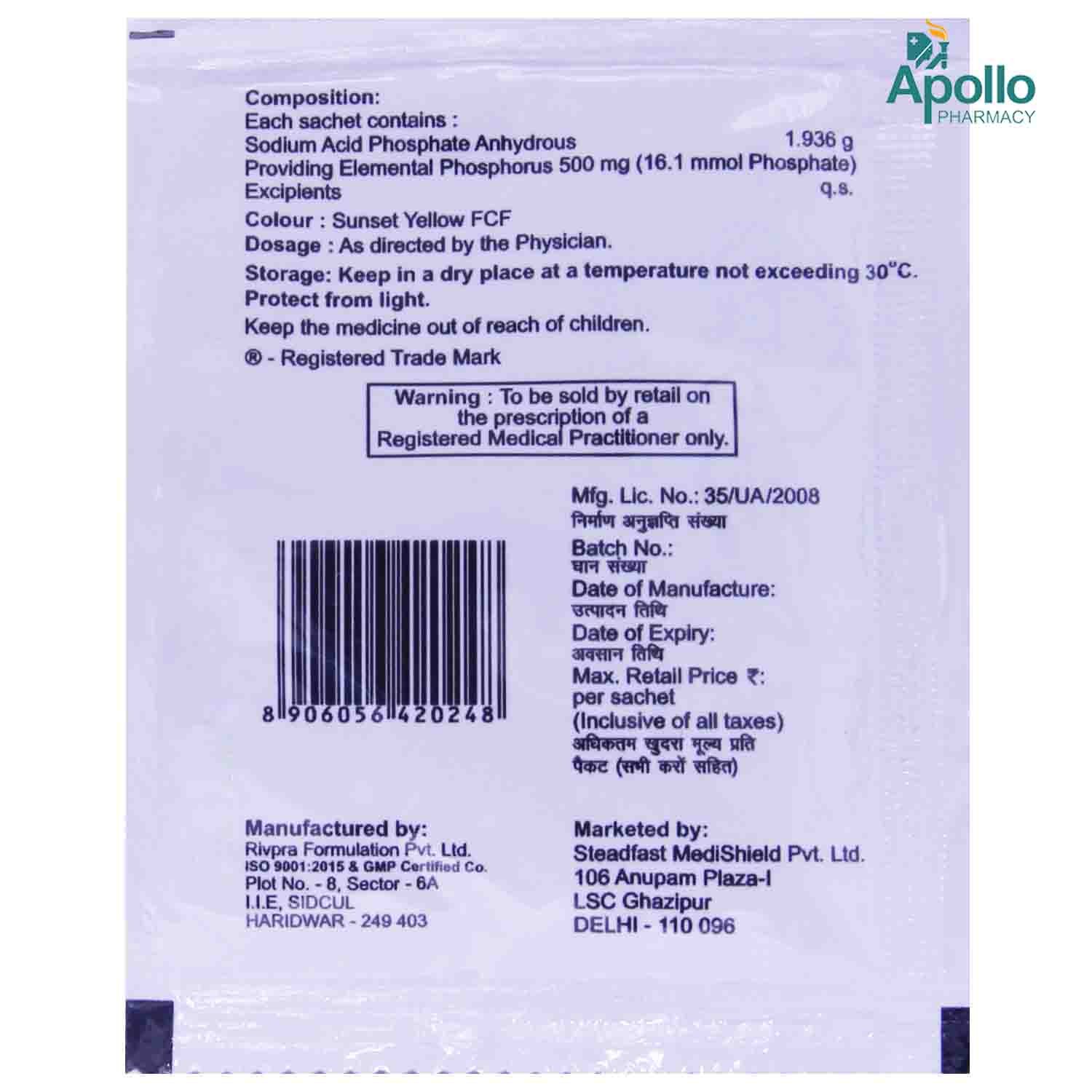
Composition :
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :

Secure Payment

Trusted by 8 Crore Indians

Genuine Products
Therapeutic Class
Country of origin
Manufacturer/Marketer address
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
FAQs
Disclaimer
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
It is unknown if alcohol interacts with Addphos Granules . Please consult your doctor.
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
Please consult your doctor if you are pregnant or if you have any concerns regarding this. Your doctor will prescribe only if the benefits outweigh the risks.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
Please consult your doctor if you are breastfeeding or if you have any concerns regarding this. Your doctor will decide whether breastfeeding women can take Addphos Granules or not.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
Addphos Granules is unlikely to affect your ability to drive. However, drive or handle machinery only if you are alert.
Liver
Consult your doctor
Please consult your doctor if you have a liver impairment or any concerns regarding this.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
Addphos Granules contains potassium; this should be taken into consideration if you have lowered kidney function. Please consult your doctor if you have kidney impairment or any concerns regarding this.
Children
Safe if prescribed
Addphos Granules should be given to children only if prescribed by the doctor.
Product Substitutes
About Addphos Granules
Addphos Granules is used to treat high blood calcium levels caused by hyperparathyroidism (overactive parathyroid glands) and multiple myelomatosis (blood cancer). Additionally, Addphos Granules is also used to treat low blood potassium due to vitamin D resistant rickets (a bone disease that does not respond to vitamin D treatment) and vitamin D resistant hypophosphatemic osteomalacia (bone softening condition).
Addphos Granules contains ‘Sodium acid phosphate’, which binds with the calcium, this helps the calcium levels go back to normal. It also helps in increasing the levels of potassium in the blood. Thereby, Addphos Granules helps in treating high calcium and low potassium levels.
You are advised to take Addphos Granules for as long as your doctor has prescribed it for you, depending on your medical condition. In some cases, you may experience common side effects such as stomach upset, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Most of these side effects do not require medical attention and will resolve gradually over time. However, you are advised to talk to your doctor if you experience these side effects persistently.
Consult a doctor before taking Addphos Granules if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Addphos Granules should be given to children only if prescribed by a doctor. Inform your doctor if you are on sodium controlled diet or if you have reduced kidney function. Keep your doctor informed about your health condition and the medicines you are taking to rule out any side effects/interactions.
Uses of Addphos Granules
Medicinal Benefits Mweb
Key Benefits
Addphos Granules is used to treat high blood calcium levels caused by hyperparathyroidism (overactive parathyroid glands) and multiple myelomatosis (blood cancer). Besides this, Addphos Granules is also used to treat low blood potassium due to vitamin D-resistant rickets (a bone disease that does not respond to vitamin D treatment) and vitamin D-resistant hypophosphatemic osteomalacia (bone softening condition). Addphos Granules binds with the calcium and makes the calcium levels go back to normal. It also helps in increasing the levels of potassium in the blood. Thereby, Addphos Granules helps in treating high calcium and low potassium levels.
Directions for Use
Side Effects of Addphos Granules
- Stomach upset
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
Drug Warnings
Do not take Addphos Granules if you are allergic to any of its components. Talk to your doctor if you have congestive heart failure, high blood pressure, sodium restrictions in your diet, pre-eclamptic toxaemia (high blood pressure during pregnancy), kidney or liver disease. Consult your doctor before taking Addphos Granules if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Addphos Granules should be given to children only if prescribed by a doctor.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Habit Forming
Special Advise
- Regular monitoring of electrolyte levels while taking Addphos Granules is advised.
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Maintain a well balanced diet containing fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Drink plenty of water. Staying hydrated lowers calcium levels and prevents kidney stones.
- Smoking can cause bone loss. Quit smoking.
- Exercise regularly as it helps promote bone health.
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
Out of StockFoslift Granules 3.2 gm
Mediart Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
₹22.5
(₹7.03/ 1gm)
13% COSTLIER

Have a query?
Buy best Health & Nutrition products by
Vlado Sky Enterprise Pvt Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Apollo Healthco Limited
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
West Coast Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Meyer Organics Pvt Ltd
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
Nutritionalab Pvt Ltd
Eris Life Sciences Ltd
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
British Biologicals
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Cipla Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Pharmed Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Modi Mundipharma Pvt Ltd
Corona Remedies Pvt Ltd
Hindustan Unilever Ltd
Indchemie Health Specialities Pvt Ltd
Apex Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Koye Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Bioceutics Inc
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
FDC Ltd
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
DR Johns Lab Pharma Pvt Ltd
Herbs Nutriproducts Pvt Ltd
Guardian Healthcare Services Pvt Ltd
Vasu Organics Pvt Ltd
Pulse Pharmaceuticals
Fourrts India Laboratories Pvt Ltd
TTK Healthcare Ltd
Raptakos Brett & Co Ltd
USV Pvt Ltd
Glanbia Performance Nutrition India Pvt Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Innovcare Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Linux Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Troikaa Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Bright Lifecare Pvt Ltd
Wockhardt Ltd
Sanofi India Ltd
Primus Remedies Pvt Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Kellogg India Pvt Ltd
Tablets India Ltd
Indoco Remedies Ltd
Medley Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Overseas Health Care Pvt Ltd
Procter & Gamble Health Ltd
Shri Balaji Overseas
Dabur India Ltd
Ordain Health Care Global Pvt Ltd
Systopic Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Daris Biocare
Health & Happiness (H&H) Trading India Pvt Ltd
Hexagon Nutrition Pvt Ltd
Nutricia International Pvt Ltd
Zee Laboratories Ltd
Aareen Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Aeronutrix Sports Products Pvt Ltd
Emami Ltd
Radicool Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Wanbury Ltd
Biovitamins Pvt Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Esmatrix Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Klm Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Lloyd Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Sain Medicaments Pvt Ltd
Septalyst Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Tas Med India Pvt Ltd
Wallace Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Biorex Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Elbrit Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Levin Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Panacea Biotec Ltd
Adret Retail Pvt Ltd
Cipla Health Ltd
Delcure Life Sciences Ltd
Femura Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Gladstone Pharma India Pvt Ltd
GlaxoSmithKline Consumer Healthcare Ltd
Kepler Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Ronyd Healthcare Pvt Ltd
SPECIALITY SUPPLEMENT
CALCIUM
IRON
VITAMIN D
COLLAGEN
VITAMIN B12
VITAMIN C
FISH OIL OMEGA
VITAMIN B
MULTIVITAMIN
Adult Nutrition Drink
ZINC
SEXUAL HEALTH SUPPLEMENT
WHEY PROTEIN
Kids Nutrition Drink
VITAMIN B9
ENERGY DRINK
SPECIALITY NUTRITION DRINK
DRY FRUIT
HERBAL JUICE
VITAMIN E
Prebiotic & Probiotic
ORS
SUGAR SUBSTITUTE
WOMEN & MOTHER NUTRITION DRINK
Chyawanprash
MAGNESIUM
Protein Bar
BREAKFAST CEREAL
Protein Powder
BIOTIN
DIABETIC NUTRITION DRINK
Honey
WEIGHT LOSS
Fat Burner
PLANT PROTEIN POWDER
VITAMIN B1
Apple Cider Vinegar
MELATONIN
APPETITE STIMULANT
Meal Replacement
Peanut Butter
AMINO ACID
Flax seed Oil
INFUSION TEA
NUT & SEED
Ashwagandha
Instant Food
OATS
Olive Oil
Mass Gainer
Pre Workout
CURCUMIN
POTASSIUM
VITAMIN A
DISKETTE
L-Carnitine
Cod Liver Oil
CREATINE
MILLETS & CEREALS
VITAMIN B6
ARGININE
COENZYME Q10
Shilajit
Appetite Suppressant
Chromium
MILK THISTLE
Glutathione
VITAMIN B2
VITAMIN K
L-Glutamine
MORINGA
GARCINIA CAMBOGIA
GREEN TEA
SPIRULINA
ALPHA-LIPOIC ACID
GLUCOSAMINE
GOKSHURA
BCAA Protein Powder
GILOY
NEEM
SAFFRON
SELENIUM
TRIPHALA
Tulsi
VITAMIN B3
VITAMIN B5
Brahmi
CANDIES
FRUIT JUICE
Face Gel
Specialty Supplements
WEIGHT GAINER
WHEAT GRASS POWDER
Frequently Bought Together
Customers Also Bought

_0.jpg?tr=q-85)