- Home
- Blog
- Women Care
Hormonal Imbalance In Women: Know The Causes, Signs And Ways To Manage It
Women Care
Hormonal Imbalance In Women: Know The Causes, Signs And Ways To Manage It
By Apollo 24|7, Published on- 22 June 2022, Updated on -20 March 2023
Share this article
0
2 likes

We often hear women complaining about hormonal imbalance. But what does it mean? Hormones are chemicals released by the glands into the blood to carry out various functions. While more than 50 hormones are released in the body, sex hormones are different for both men and women. For instance, the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone released by the ovaries are responsible for regulating periods and maintaining pregnancy. While some hormone levels keep changing with age, fluctuations in other hormones may require medical attention. You will be surprised to know around 50% of women experience hormonal imbalance at least once in their lives, which affects their overall health.
What are the signs of hormonal imbalance in women?
The signs of hormonal imbalance can vary for each individual. However, the most common signs include:
- Mood swings
- Hot flashes
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Inability to sleep (insomnia)
- Irregular periods (missing, frequent or stopped periods)
- Increased menstrual cramps (pain in the abdomen, lower back and legs)
- Low sex drive (low libido)
- Vaginal dryness
- Increased hair growth on the face, chest and back (hirsutism)
- Thinning of hair and hair loss
- Drying of skin
- Persistent acne
- Pain or stiffness in the joints
- Weak bones
- Infertility
.jpg)
What are the causes of hormonal imbalance?
Some of the common causes of hormonal imbalance in women include:
1. Menopause: Most women attain menopause in the age group of 45 to 55 years. Menopause occurs when the ovaries stop releasing eggs and the body stops producing sex hormones, resulting in a hormonal imbalance.
2. Stress: Research shows that excessive stress can prevent the release of eggs from the ovaries (anovulation), ultimately resulting in absence of periods (amenorrhoea).
3. Pregnancy: Women experience a dramatic rise in estrogen and progesterone levels after getting pregnant. These hormones help in sustaining the pregnancy and nourish the baby. This is a temporary change as the levels of hormones get back to normal after the baby is delivered.

4. Thyroid disorders: Studies show that hypothyroidism lowers the levels of estradiol, a type of estrogen that helps women conceive. It has also been found that abnormally high or low levels of thyroid hormone can cause irregular, heavy or absence of periods.
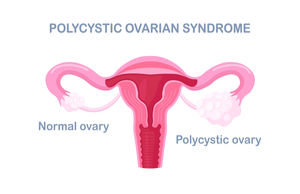
5. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a condition in which the ovaries start producing excessive male sex hormones (androgens), thus resulting in an imbalance.
Recommended read: Menopause: The different stages
How to deal with hormonal imbalance?
Self-management measures that can help in dealing with hormonal imbalance in women include:
- Managing weight: Research shows that losing even 10% of their current body weight can help in the regulation of periods and increase the likelihood of getting pregnant. Practise any moderate-intensity exercise such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for 30 minutes, 5 days a week to maintain a healthy weight.
- Making dietary changes: Adding soybeans, chickpeas, lentils, flaxseeds, whole grains, fruits, and green vegetables to the diet can help reduce the frequency of hot flashes. Avoid the consumption of sugary foods and beverages as they can add extra kilos.
-
Getting enough sleep: Sleep for at least 7 to 8 hours a day to ensure overall well-being.
.jpg)
- Dealing with hot flashes: Avoid the consumption of hot beverages, caffeine, spicy food, and alcohol as they can trigger hot flashes. Practice deep breathing, meditation, and stay in a cooler environment to reduce the frequency of hot flashes to almost half.
- Relieving vaginal dryness: Use estrogen vaginal gels or rings that can be applied inside the vagina to reduce dryness.
- Improving mental health: Practice mindfulness, and meditation, and indulge in things that give you joy as it would help in reducing stress and keep your hormone levels balanced.

Recommended read: Health Tips For Women Living With PCOS
Medical therapies that can help manage the hormonal imbalance are:
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT): In HRT, the affected woman is given supplements of progesterone and estrogen to maintain bone health, skin temperature, vaginal moistness, and relieve hot flashes and mood swings.
- Hormonal birth control: Doctors may prescribe estrogen and/or progesterone-containing medications to regulate the period cycle and relieve symptoms such as acne and unwanted hair growth.
- Androgen-blockers: In some cases, the doctor may also prescribe anti-androgen medicines to block the activity of androgens, which are otherwise responsible for acne, hair loss, and unwanted facial hair growth.
While for most women hormonal imbalance is temporary, some of them may need medical attention. Women experiencing signs of hormonal imbalance should consult a gynaecologist for further investigation.
Consult An Apollo Gynaecologist
Medically reviewed by Dr Sonia Bhatt.
Services
Women Care
Leave Comment
Services
Recommended for you

Women Care
Waxing Intimate Areas: Should You Even Do It?
Waxing intimate areas is a topic that is surrounded by many myths and misconceptions. In truth, waxing your intimate areas carries both risks and benefits. If you do choose to go this way, there are certain precautions you must take to minimise the risks.

Women Care
5 Myths About Pregnancy You Must Stop Believing Right Away!
Pregnancy is a transformative time in any woman’s life. However, this transition often gets difficult due to the numerous myths and misconceptions surrounding pregnancy. his article covers the top 5 pregnancy myths and the facts behind them.

Women Care
Third Trimester Diet: Here’s What To Eat And What To Avoid
It's essential to meet your daily nutritional needs during the third trimester of your pregnancy to ensure the proper growth and development of your child. Here is a list of foods that you should eat and avoid during this crucial period of your pregnancy.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.

